Cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, targeting every layer of digital communication—from applications and servers to the very core of internet protocols. Among the most notorious network-level threats is the Smurf attack, a dangerous form of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack that can overwhelm networks and take entire online infrastructures offline.
Despite its harmless-sounding name, smurfing attack techniques can cause serious disruption to organizations, businesses, and even critical services. Understanding how they work is essential for strengthening defense strategies against modern cyberattacks.
This complete guide explains what is a Smurf attack, how it works, its devastating consequences, and how to prevent it effectively.
What is a Smurf Attack?

A Smurf attack is a network-based DDoS attack that exploits vulnerabilities in the Internet Protocol (IP) and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). Attackers flood networks with spoofed ICMP “echo request” messages (pings), tricking connected devices into responding simultaneously.
The result? A massive surge of network traffic that overwhelms the target, causing a denial of service.
So, the smurf attack meaning can be defined as:
A cyberattack in which attackers send spoofed ICMP requests to an entire network using broadcast addressing, causing multiple devices to unknowingly bombard a victim with traffic — overload occurs, making servers and services unreachable.
The attack is named after the malware tool “Smurf,” first used in the 1990s — small but capable of swarming and overwhelming its target.
How a Smurf Attack Works — Step-by-Step Breakdown

To better understand what is a smurf attack, let’s break down the technical steps involved.
Step One: Spoofing an IP Address
The attacker forges the source IP address in the packet to make it appear as though it originated from the attacker’s victim.
Step Two: Sending ICMP Echo Requests
The forged packet contains a ping request (ICMP echo) and is sent to a network’s broadcast address (e.g., 192.168.1.255).
A broadcast address ensures every device in that network receives the request.
Step Three: Traffic Amplification
All responding devices send their echo replies back to the spoofed victim, not the attacker.
This repetition creates:
- Traffic amplification
- A flood of responses
- A complete denial of service
The Infinite Loop of Network Flooding
Because of the ICMP nature of the request, traffic can keep circulating rapidly,
paralyzing the victim’s network resources.
A small packet triggers thousands of responses — that’s why smurfing attack scenarios are both powerful and highly disruptive.
Why Smurf Attacks Are So Dangerous
The attacker doesn’t need powerful systems — only a network configured incorrectly.
A successful Smurf attack can lead to:
- Network shutdowns
- Server crashes
- Loss of business productivity
- Communication failure
- Service outage for hours or even days
Often, smurf attack activity is a smokescreen, executed alongside:
- Data breaches
- Unauthorized access
- Intellectual property theft
While IT staff struggles with network downtime, malicious actors may steal sensitive information unnoticed.
How a Smurf Attack Spreads
Smurf malware often arrives through:
- Malicious email links
- Downloads from unverified websites
- Trojan-bundled software
- Infected USB drives
It may remain dormant until remotely triggered, frequently alongside rootkits that provide attackers persistent access to systems.
Once deployed, the program uses the infected machine to propagate the attack — turning it into a bot participating in larger distributed attacks.
Smurf Attack vs. Fraggle Attack
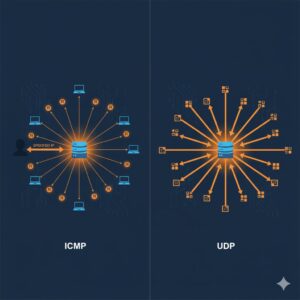
Cybercriminals often deploy variations of DDoS techniques.
A closely related attack is the Fraggle attack.
| Attack Type | Protocol Used | Key Difference |
| Smurf Attack | ICMP Echo Requests | Ping floods to broadcast address |
| Fraggle Attack | UDP Packets | Usually targets ports like 7 (Echo) or 19 (Chargen) |
Both leverage traffic amplification and broadcast responses, but the protocol used differs.
Real-World Impact of Smurf Attacks
Smurf attacks can impact:
- Government communication systems
- Banking networks
- Corporate servers
- Educational institutions
- Healthcare systems
- Cloud computing platforms
Even a short-lived attack can cause:
- Financial loss due to shutdowns
- Damage to an organization’s reputation
- Loss of customer trust
- Potential legal consequences
The simplicity and power of smurfing attack techniques make them appealing to cybe
Also Read: What Is Stuxnet? A Complete Explanation of the World’s First Cyber Weapon
How to Detect a Smurf Attack
Knowing the early indicators can prevent damage:
- Sudden network congestion
- Multiple ICMP responses with the same source
- Servers freezing or crashing
- Rapid spike in bandwidth usage
- System logs filled with ICMP activity
Network monitoring and intrusion detection solutions are critical for spotting anomalies before the attack spreads.
How to Prevent Smurf Attacks
Although the smurf attack meaning may sound complex, the solution is simple cyber hygiene and proper configuration.
Here are effective prevention techniques:
Disable IP Broadcasting
Most networks no longer require broadcast messaging.
Routers should have IP-directed broadcasts disabled.
Block ICMP Echo Requests
Firewalls must be configured to block:
- Incoming ICMP requests from outside
- Broadcast traffic that could be abused
Harden Network Devices
Ensure routers, switches, and host devices:
- Do not respond to broadcast IP requests
- Implement strict traffic filtering
Maintain Real-Time Monitoring
Constant monitoring prevents small issues from becoming flood attacks.
Regular Network Audits
Organizations should:
- Perform penetration tests
- Patch firmware vulnerabilities
- Fix misconfigurations quickly
Educate Admins and Employees
Human error or overlooked settings are the biggest weaknesses.
Training and awareness reduce cyber exposure.
When these protections are in place, smurfing attacks become much harder to execute.
Why Are Smurf Attacks Still Relevant Today?
Even though internet infrastructure has evolved, not all networks are properly secured.
Older hardware and legacy systems still exist in:
- Industrial facilities
- Small enterprises
- Government organizations
Cybercriminals exploit these weak spots.
As the number of internet-connected devices (IoT) grows, more potential endpoints become vulnerable. This keeps smurf attack techniques alive and dangerous.
Conclusion
A Smurf attack may sound playful, but the consequences are anything but.
Understanding what is smurf attack, how it exploits ICMP and broadcast traffic, and its potential to take down entire networks is crucial in today’s threat landscape.
Proper configuration, proactive monitoring, and strong cybersecurity hygiene can effectively prevent these amplification-based DDoS attacks.
Organizations must stay vigilant because a single overlooked router setting can make the entire network vulnerable.
Defend today — because attackers only need one mistake to strike.
FAQs
What is a Smurf attack in simple terms?
It is a cyberattack where attackers flood a network with spoofed ICMP requests, causing so many responses that the target system becomes overloaded and shuts down.
Why is it called a Smurf attack?
The original malware tool behind the attack was named “Smurf,” referencing the idea of many tiny attackers overwhelming a large target.
Is a Smurf attack a type of DDoS attack?
Yes, it is a form of distributed denial-of-service attack that uses broadcast traffic to amplify the attack.
Can a Smurf attack cause data loss?
Directly, it causes service disruption — but attackers may use it as a distraction to perform data theft during downtime.
How can I protect my network from Smurf attacks?
Disable IP broadcast addressing, restrict ICMP traffic, and monitor all network traffic for unusual volume spikes.




