As digital finance continues to grow, protecting cryptocurrency has become just as important as acquiring it. With cyber threats, exchange hacks, phishing scams, and malware incidents becoming more frequent, relying solely on online platforms to store crypto assets can be risky. This is where understanding what is a hardware wallet becomes essential for anyone serious about long-term crypto security.
A hardware wallet offers one of the most secure ways to protect digital assets by keeping critical information offline. This guide explains what are hardware wallets, how they function, why they are considered safer than online wallets, and how users can follow best practices to protect their investments.
What Is a Hardware Wallet?

A hardware wallet is a physical device designed to securely store a user’s private cryptographic keys offline. These private keys are what allow access to cryptocurrency stored on the blockchain. Unlike traditional wallets that hold cash or cards, a hardware wallet does not store cryptocurrency itself. Instead, it stores the keys that prove ownership of digital assets.
When people ask what is a hardware wallet, the simplest answer is that it is a cold storage solution for cryptocurrencies. Cold storage means the wallet remains disconnected from the internet when not actively in use, significantly reducing the risk of hacking or unauthorized access.
Most hardware wallets resemble small USB devices and can connect to a computer or mobile device only when a transaction needs to be signed. Once disconnected, the private keys remain isolated from online threats.
What Are Hardware Wallets Used For?
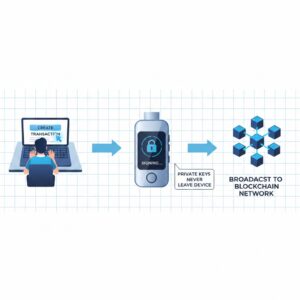
Hardware wallets are used to securely manage, send, receive, and store cryptocurrencies across multiple blockchains. Modern hardware wallets support a wide range of digital assets, allowing users to manage different tokens from one device.
Key uses include:
Secure long-term storage of cryptocurrency
Signing transactions without exposing private keys
Managing multiple crypto assets in one place
Reducing reliance on third-party exchanges
For investors holding significant amounts of crypto, hardware wallets are often considered essential.
Types of Cryptocurrency Wallets Explained
To fully understand hardware wallets, it helps to compare them with other types of wallets.
Hot Wallets
Hot wallets are connected to the internet and include mobile apps, desktop wallets, and exchange wallets. They are convenient for frequent trading but are more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Cold Wallets
Cold wallets operate offline and include paper wallets and hardware wallets. Among cold storage options, hardware wallets are the most practical because they combine offline security with ease of use.
This distinction explains why hardware wallets are often preferred for storing larger balances or assets meant for long-term holding.
Why Hardware Wallets Are More Secure
The main reason hardware wallets are considered highly secure is their offline nature. Since private keys never leave the device, hackers cannot access them through malware, phishing attacks, or compromised websites.
Additional security benefits include:
Isolation from internet-based threats
Transaction verification on the device itself
Protection from keylogging and screen capture attacks
Reduced risk from exchange breaches
Even when a hardware wallet is connected to an internet-enabled device, the private keys remain inside the wallet and never appear on the connected computer or phone.
What is Cryptographic Keys
Cryptocurrencies rely on cryptographic keys to function. These keys are long strings of characters generated through advanced encryption.
Public Keys
Public keys act like account numbers. They can be shared with others to receive funds and are visible on the blockchain.
Private Keys
Private keys function like secret passwords. Anyone with access to a private key can control the associated cryptocurrency. This is why protecting private keys is critical.
The phrase “not your keys, not your crypto” highlights the importance of owning and controlling private keys yourself rather than relying on third-party platforms.
How Does a Hardware Wallet Work?
Many beginners ask how does a hardware wallet work in real-world usage. The process is secure yet straightforward.
When a hardware wallet is set up, it generates private keys within the device. These keys never leave the wallet. When a user wants to make a transaction, the following steps occur:
The user initiates a transaction on a connected device
The transaction data is sent to the hardware wallet
The wallet signs the transaction internally using the private key
The signed transaction is returned and broadcast to the blockchain
At no point are the private keys exposed to the internet or external software.
Transaction Signing Explained
Transaction signing is the core function of a hardware wallet. Signing confirms that the transaction is authorized by the owner of the private keys.
The wallet’s internal processor performs this operation securely. Some hardware wallets include small screens that display transaction details, allowing users to verify recipient addresses and amounts before approving.
This added verification step protects users from malware that might attempt to alter transaction details.
Managing Multiple Assets with Hardware Wallets
Modern hardware wallets support multiple blockchains and hundreds of cryptocurrencies. This allows users to manage diverse portfolios without juggling multiple wallets.
Users can interact with decentralized applications, stake assets, or manage tokens while still keeping their private keys offline.
Backup and Recovery Features
Hardware wallets include backup options to protect against loss or damage. During setup, users are provided with a recovery phrase, often consisting of twelve to twenty-four randomly generated words.
This recovery phrase allows users to restore access to their assets if the hardware wallet is lost, stolen, or damaged. Protecting this phrase is just as important as protecting the wallet itself.
Best Practices for Hardware Wallet Security
Even though hardware wallets are secure by design, users should follow best practices to maximize protection.
Store the device in a secure, dry place
Never share recovery phrases or private keys
Avoid storing recovery phrases digitally without encryption
Use strong PIN codes
Verify transaction details on the device screen
Proper handling ensures that even physical theft does not result in asset loss.
Buying a Hardware Wallet Safely
When purchasing hardware wallets, users should always buy directly from reputable manufacturers or authorized sellers. Used or tampered devices can contain malicious modifications that compromise security.
Signs of tampering include broken seals or missing security features. If anything appears suspicious, the device should not be used.
Hardware Wallets vs Exchange Storage
Many users leave cryptocurrency on exchanges for convenience. However, exchange wallets store private keys on behalf of users, creating a single point of failure.
History has shown that exchanges can be hacked, frozen, or shut down. Hardware wallets eliminate this risk by giving users full control over their assets.
Limitations of Hardware Wallets
While hardware wallets offer strong security, they are not without drawbacks.
They require careful physical storage
There is a learning curve for beginners
Transactions take slightly longer than hot wallets
Despite these limitations, the benefits often outweigh the inconveniences for serious investors.
Who Should Use a Hardware Wallet?
Hardware wallets are ideal for:
Long-term crypto investors
Users holding large balances
Security-conscious individuals
Those seeking independence from exchanges
Even beginners can benefit from learning what are hardware wallets early in their crypto journey.
Conclusion
Understanding what is a hardware wallet and how does a hardware wallet work is crucial in today’s digital asset landscape. Hardware wallets provide one of the safest methods to protect cryptocurrencies by keeping private keys offline and under the user’s full control.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, relying on secure storage solutions is no longer optional. Hardware wallets empower users to take ownership of their assets, reduce risk, and participate in the crypto ecosystem with confidence.
For anyone serious about long-term crypto security, a hardware wallet is not just a tool but a foundational safeguard.
FAQs
What is a hardware wallet used for?
A hardware wallet is used to securely store private keys offline and manage cryptocurrency transactions safely.
Are hardware wallets completely safe?
They offer very high security, but users must still protect recovery phrases and follow best practices.
Can hardware wallets be hacked?
Remote hacking is extremely difficult since private keys never leave the device, but physical theft combined with poor security practices can pose risks.
Do hardware wallets store cryptocurrency?
No, they store private keys that grant access to cryptocurrency on the blockchain.
Is a hardware wallet suitable for beginners?
Yes, especially for those planning to hold cryptocurrency long-term and prioritize security.




