Digital security has become one of the biggest concerns for individuals and businesses in 2026. Almost every activity—banking, work, shopping, communication, and data storage—now happens online. As digital usage grows, cybercriminals also become more advanced in how they attack user accounts and steal sensitive information.
Traditional login systems, especially those based only on usernames and passwords, are no longer strong enough to protect modern digital environments. Password leaks, phishing attacks, and credential stuffing have made account takeovers more common than ever.
This blog explains the different types of authentication methods used in 2026, compares their security levels, and clearly answers one key question: Which type of authentication is the most secure in 2026? The goal is to help individuals and businesses make informed, practical security decisions.
What Is Authentication?
Authentication is the process of verifying that a user is who they claim to be before allowing access to a system, application, or data. It acts as a gatekeeper between users and digital resources.
In simple terms, authentication answers one question: “Are you really who you say you are?”
Over time, authentication has evolved as threats have increased. Earlier systems relied only on passwords. Today, authentication uses multiple layers such as devices, biometrics, and cryptographic keys to confirm identity more securely.
Authentication is important because it:
- Prevents unauthorized access
- Protects personal and business data
- Reduces the risk of fraud and identity theft
- Helps organizations meet security and compliance requirements
Why Authentication Security Matters More in 2026

Authentication security is more critical in 2026 than ever before due to major changes in how technology is used and how attacks are carried out.
First, data breaches have increased in scale and frequency. Attackers no longer target just large companies; small businesses and individual users are also frequent victims.
Second, remote work and cloud-based tools are now standard. Employees access company systems from multiple locations and devices, increasing the attack surface.
Third, cybercriminals use automation and AI-powered tools to launch faster and smarter attacks. Password guessing, phishing emails, and fake login pages can now be created at scale.
Finally, governments and regulatory bodies require stronger identity protection to safeguard user data. Weak authentication can lead to legal and financial penalties.
Key Factors That Define a “Secure” Authentication Method
A secure authentication method is not defined by just one feature. Instead, it is evaluated using multiple security and usability factors.
- Resistance to phishing attacks
A secure method should not rely on information that can be easily tricked or stolen through fake websites or emails. - Protection against credential theft
Authentication should avoid reusable secrets like passwords that can be leaked or reused. - Balance between security and usability
If authentication is too complex, users may try to bypass it, reducing overall security. - Scalability for businesses
Secure authentication should work across many users, devices, and systems without becoming difficult to manage. - Compliance with modern security standards
Authentication methods should align with current cybersecurity frameworks and best practices.
Types of Authentication Methods Used in 2026
Password-Based Authentication
Password-based authentication is the oldest and most widely used method. Users prove their identity by entering a secret password that matches stored credentials.
While passwords are easy to implement, they have serious security limitations. Users often reuse passwords, choose weak combinations, or fall victim to phishing attacks.
- Vulnerable to brute-force and credential-stuffing attacks
- Easily compromised through phishing
- Difficult for users to manage securely
- No built-in protection if the password is stolen
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)

Two-factor authentication improves security by requiring two different types of verification. Typically, this includes something the user knows (password) and something they have (OTP or device).
2FA significantly reduces the risk of account compromise compared to passwords alone, but it is not completely immune to attacks.
- Adds an extra layer beyond passwords
- Common methods include SMS codes and authenticator apps
- Can still be vulnerable to SIM swapping or phishing
- Widely used for consumer and business accounts
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
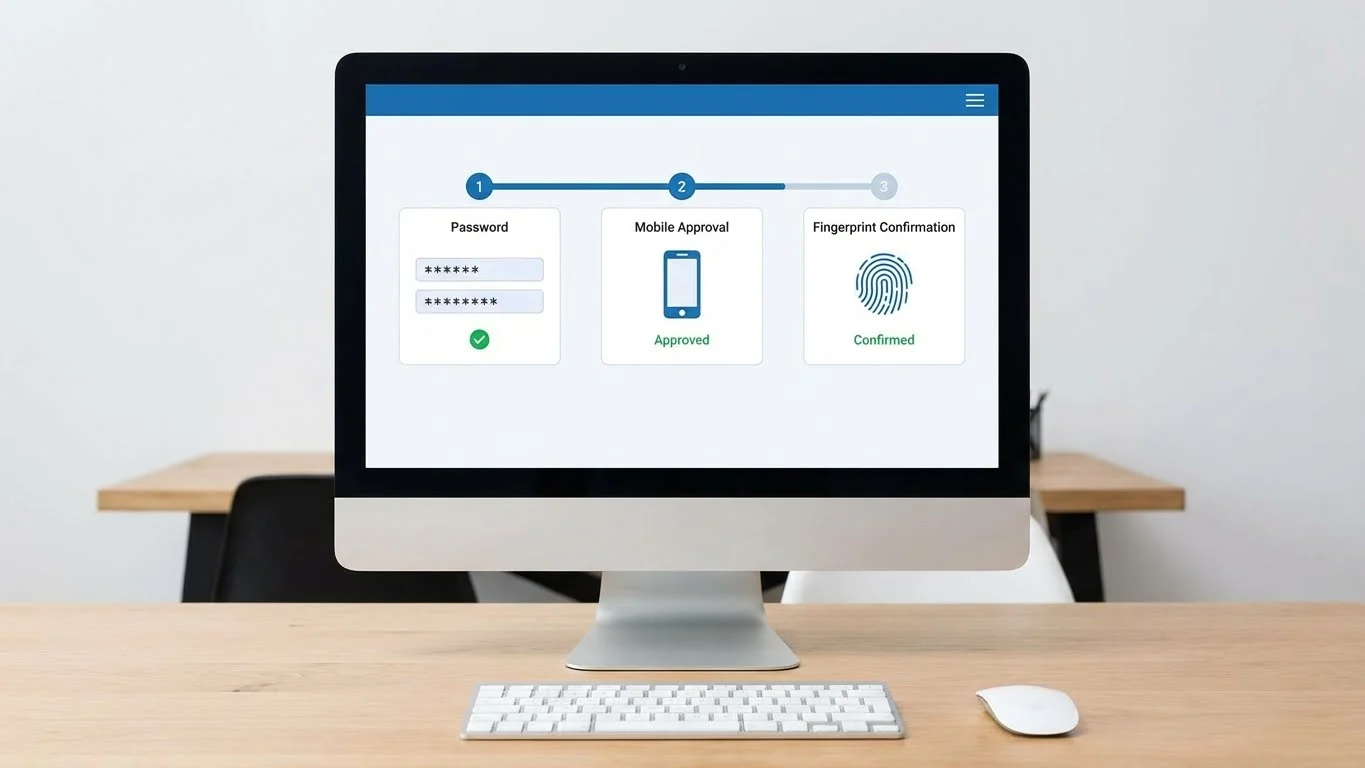
Multi-factor authentication goes beyond two factors and uses multiple independent verification methods. These factors usually include a mix of passwords, devices, and biometrics.
MFA is considered a strong defense against most common attacks because compromising multiple factors at once is difficult.
- Combines multiple identity verification factors
- Strong protection against unauthorized access
- Used widely in enterprise environments
- Can be complex if not implemented carefully
Biometric Authentication

Biometric authentication verifies identity using unique physical traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
Biometrics remove the need to remember passwords, but they raise concerns about privacy and data storage.
- Difficult to fake or guess
- Fast and user-friendly
- Biometric data cannot be changed if compromised
- Requires secure storage and encryption
Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication removes passwords completely from the login process. Instead, it relies on secure devices, cryptographic keys, or biometric verification.
This method is designed to eliminate the biggest weakness in authentication: stolen passwords.
- No passwords to steal or reuse
- Strong protection against phishing
- Often uses secure device-based verification
- Gaining rapid adoption in modern systems
Hardware-Based Authentication
Hardware-based authentication uses physical devices such as security keys or smart cards to verify identity. These devices store cryptographic keys that never leave the hardware.
This method is highly secure because attackers cannot access the authentication secret remotely.
- Extremely resistant to phishing
- Requires physical possession of the device
- Used in high-security environments
- Minimal risk of remote compromise
Comparison of Authentication Methods by Security Level
When comparing authentication methods, clear differences emerge based on attack resistance and reliability.
- Password-based authentication provides the weakest security
- 2FA improves protection but still has known vulnerabilities
- MFA offers strong security when implemented correctly
- Biometric methods enhance convenience but need secure handling
- Passwordless and hardware-based authentication provide the highest resistance to modern attacks
Which Type of Authentication Is the Most Secure in 2026?
In 2026, passwordless authentication combined with hardware-based security is considered the most secure approach.
This method removes passwords entirely and relies on cryptographic keys stored securely on trusted devices. Since there are no passwords to steal or reuse, phishing and credential theft become largely ineffective.
Security experts favor this approach because it:
- Eliminates password-related attacks
- Uses strong cryptographic verification
- Requires physical device presence
- Reduces human error
In high-risk environments, passwordless authentication is often combined with biometrics or MFA for additional protection.
Best Authentication Strategy for Businesses in 2026
The best authentication strategy is not always a single method but a layered approach based on risk levels.
- Low-risk systems may use MFA
- Sensitive systems should use passwordless or hardware-based methods
- User training is essential to prevent social engineering
- Authentication policies should be reviewed regularly
Common Authentication Mistakes to Avoid
Many organizations weaken their security due to poor authentication practices.
- Relying only on passwords
- Using outdated authentication technologies
- Ignoring usability, leading users to bypass controls
- Failing to update authentication policies regularly
Conclusion
Authentication security is no longer optional in 2026. As cyber threats become more advanced, relying on outdated login methods puts users and businesses at serious risk.
Among all available options, passwordless and hardware-based authentication offer the highest level of security today. They remove passwords, resist phishing, and significantly reduce account compromise risks.
Upgrading authentication methods is one of the most effective steps organizations and individuals can take to protect their digital future.




