Cybersecurity threats have become more advanced and more frequent. Password leaks, phishing attacks, and unauthorized account access are no longer rare events. Many people still depend on passwords alone to secure their accounts, even though passwords can be guessed, reused, or stolen easily.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is designed to solve this problem by adding extra layers of verification. Instead of relying on one method of authentication, MFA requires users to prove their identity using multiple factors. This approach greatly improves security and helps protect sensitive data in today’s digital environment.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication?
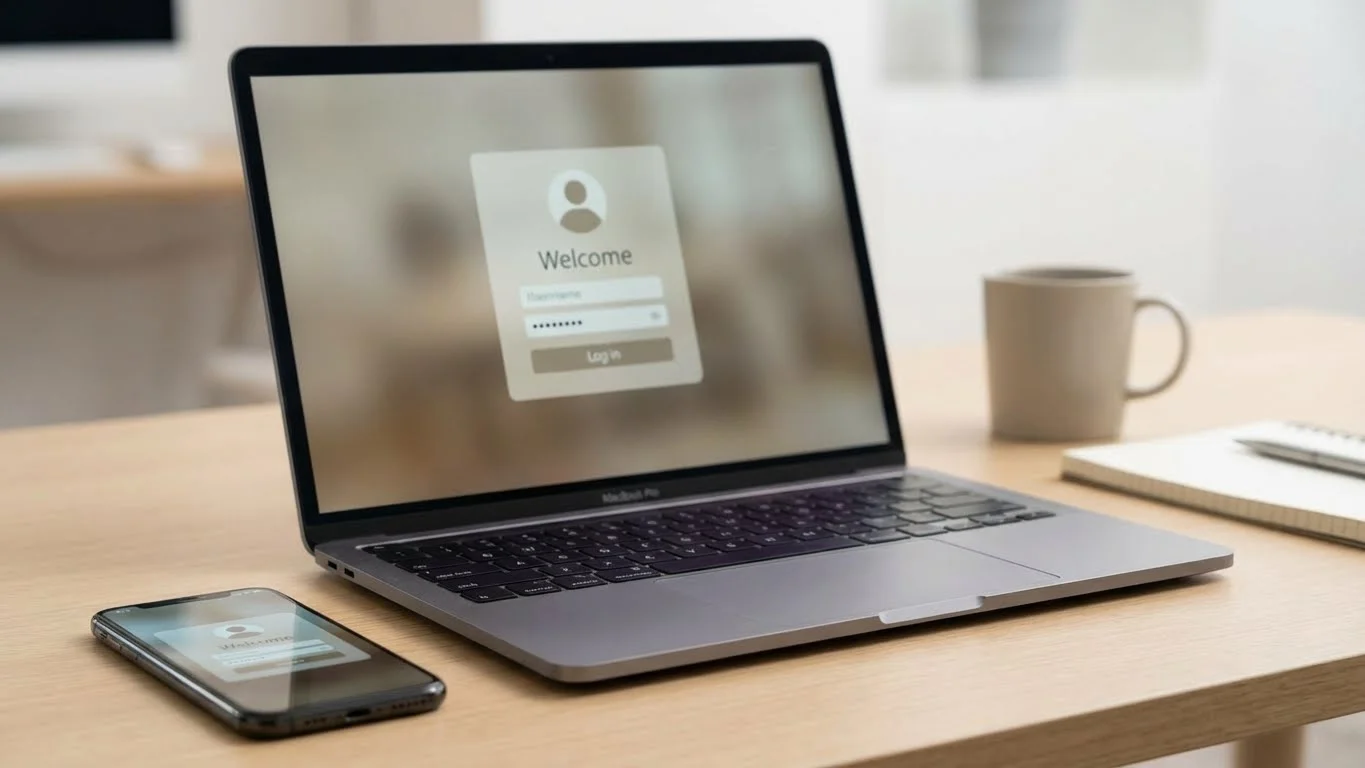

Multi-Factor Authentication is a security mechanism that requires users to verify their identity using two or more different authentication factors before accessing a system, application, or account. These factors are independent of one another and are designed to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Key characteristics of MFA include:
- It uses more than one authentication method
- Each factor belongs to a different security category
- It protects accounts even if one factor is compromised
MFA goes beyond traditional password-based security and is now widely used across personal, business, and enterprise systems.
How Multi-Factor Authentication Works
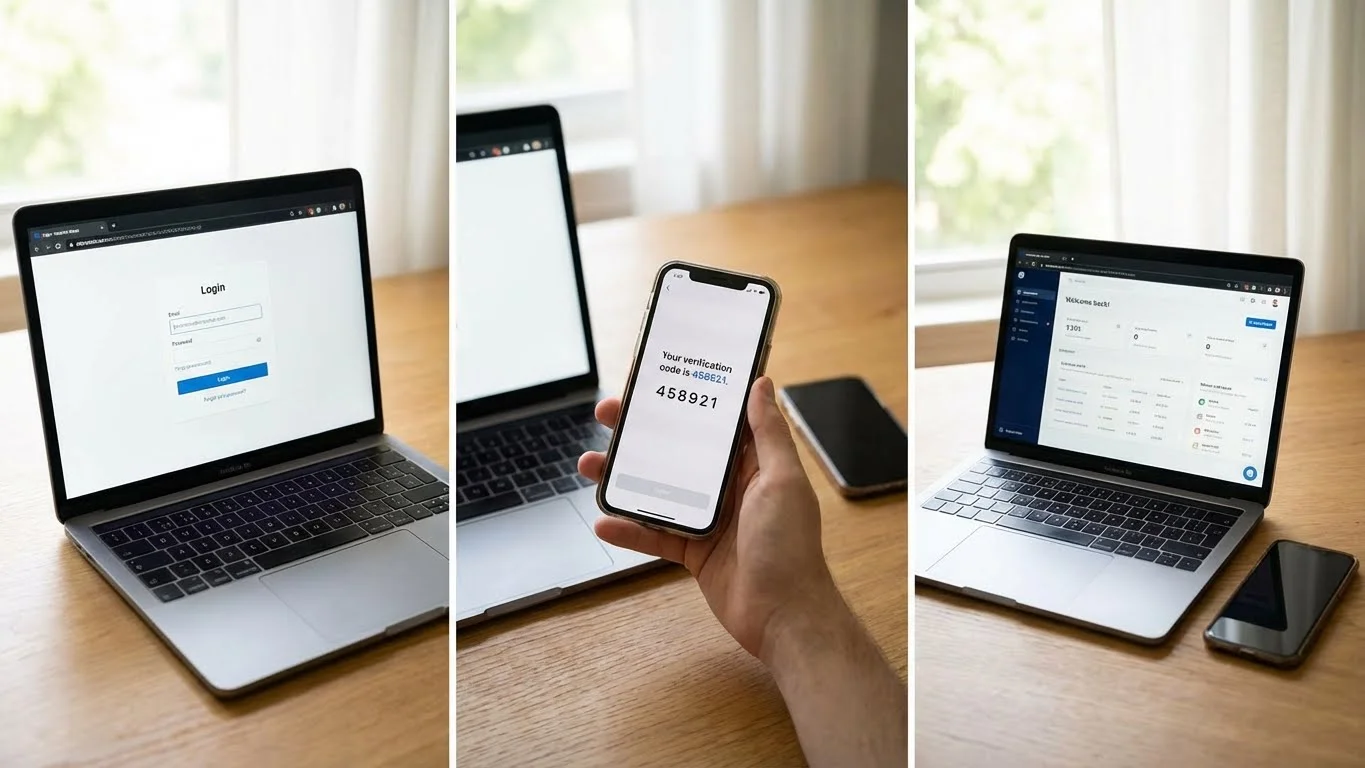
Multi-Factor Authentication works by verifying a user’s identity through multiple steps during the login process. Each step confirms a different aspect of who the user is or what they have.
The general working process includes:
- The user enters a username and password
- The system requests an additional authentication factor
- The user completes the required verification step
- Access is granted only after all checks are successful
This layered verification ensures that access is denied if any required factor fails, making it much harder for attackers to break in.
Types of Authentication Factors
Authentication factors are grouped into categories based on how identity is verified.
1. Something You Know
This factor is based on information that only the user should know. It is the most common form of authentication.
Examples include:
- Passwords
- PINs
- Security question answers
Although widely used, this factor alone is not sufficient because such information can be stolen or guessed.
2. Something You Have
This factor relies on a physical or digital item that the user possesses.
Common examples include:
- One-time passwords sent to a phone
- Authentication apps on mobile devices
- Hardware security tokens
- Email-based verification codes
This factor improves security by requiring access to a specific device or item.
3. Something You Are
This factor is based on biometric traits that are unique to each individual.
Examples include:
- Fingerprints
- Facial recognition
- Voice patterns
- Iris scans
Biometric authentication is difficult to duplicate and provides strong identity verification when used correctly.
Common MFA Methods Explained

MFA can be implemented using different methods depending on security needs and user experience requirements.
Common MFA methods include:
- SMS-based authentication, where a one-time code is sent to a phone number
- Authenticator apps, which generate time-based verification codes
- Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition
- Hardware tokens, which generate or store secure authentication data
- Push notifications, allowing users to approve or deny login attempts
Each method provides an additional layer of security beyond passwords.
Why Multi-Factor Authentication Matters

Passwords alone are no longer reliable protection. Many cyberattacks succeed simply because attackers obtain login credentials through phishing or data breaches.
MFA matters because:
- Stolen passwords are not enough to access accounts
- It reduces the success of phishing attacks
- It protects sensitive and personal data
- It limits damage even if credentials are compromised
By requiring multiple proofs of identity, MFA strengthens overall security.
Key Benefits of Using Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA offers several important advantages for both individuals and organizations.
Key benefits include:
- Stronger account protection
- Reduced risk of data breaches
- Improved trust among users and customers
- Better security for remote access
- Support for compliance and security standards
These benefits make MFA an essential security practice.
Risks of Not Using MFA
Not using MFA leaves systems vulnerable to common cyber threats.
Risks include:
- Account takeovers
- Financial fraud
- Identity theft
- Exposure of confidential data
- Damage to brand reputation
Without MFA, a single stolen password can lead to serious consequences.
MFA vs Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
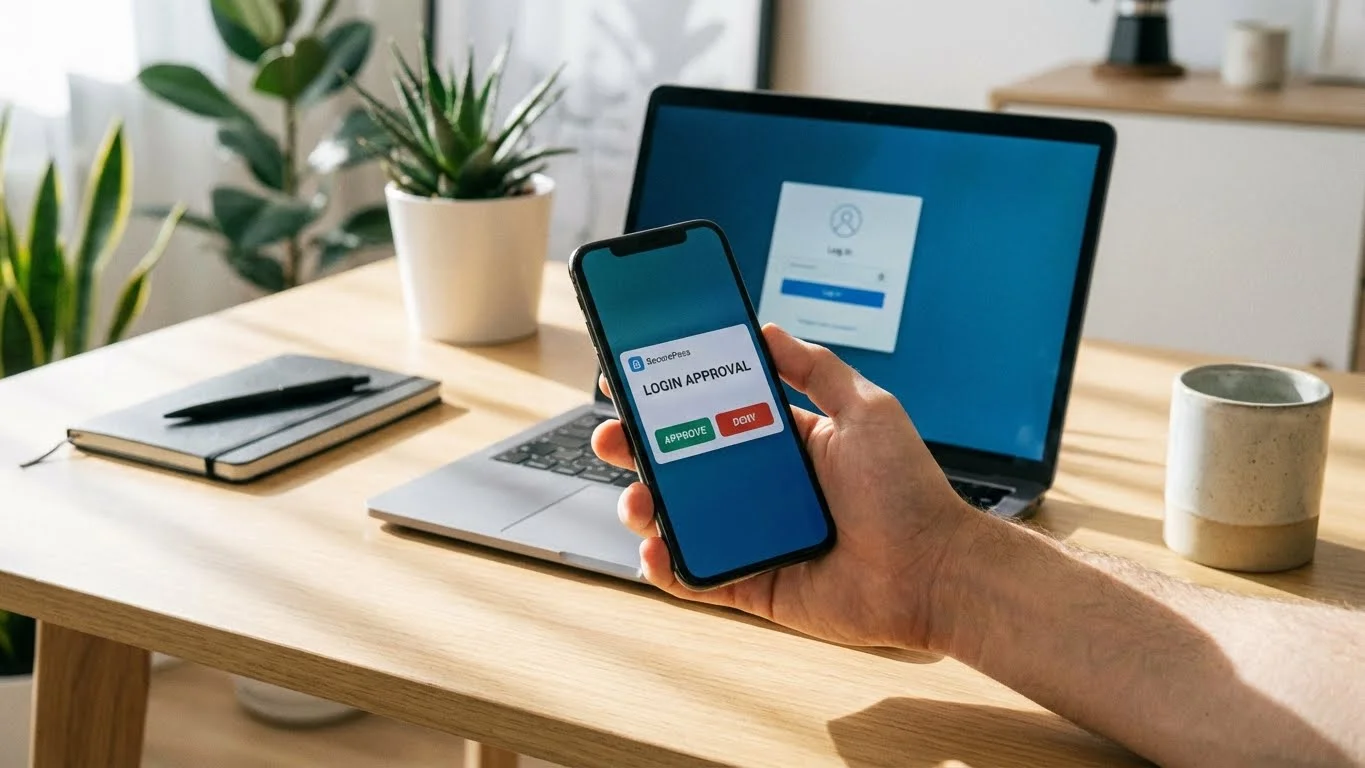

Two-Factor Authentication is a specific type of MFA that uses exactly two authentication factors. MFA, on the other hand, can use two or more factors.
Key differences include:
- 2FA is limited to two steps
- MFA allows greater flexibility
- MFA provides stronger security for high-risk environments
While 2FA is suitable for basic protection, MFA is better for systems handling sensitive data.
Where Multi-Factor Authentication Is Commonly Used
MFA is widely used in environments where security is critical.
Common use cases include:
- Email and cloud services
- Banking and financial platforms
- Healthcare systems
- Corporate and enterprise networks
- E-commerce and customer accounts
These systems often store sensitive information, making MFA necessary.
Challenges and Limitations of MFA
Although MFA improves security, it also comes with certain challenges.
Common limitations include:
- Additional login steps may affect user convenience
- Implementation and maintenance costs
- Dependence on devices or network access
- Accessibility challenges for some users
- Risk of account lockouts without backup options
Proper planning can help minimize these issues.
Best Practices for Implementing MFA
Effective MFA implementation requires thoughtful planning.
Best practices include:
- Using strong and diverse authentication factors
- Avoiding reliance on a single method
- Providing backup authentication options
- Educating users on secure login practices
- Regularly reviewing security configurations
These steps help ensure MFA remains both secure and usable.
How to Choose the Right MFA Solution
Choosing the right MFA solution depends on security needs and user requirements.
Important considerations include:
- Type and size of the organization
- Sensitivity of data being protected
- User experience and accessibility
- Cost and scalability
- Compatibility with existing systems
A balanced approach leads to successful adoption.
Conclusion
Multi-Factor Authentication is a powerful and practical solution for modern security challenges. By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA significantly reduces the risks associated with password-based systems. While it may add a small extra step to the login process, the protection it provides is far more valuable. In a world where digital threats continue to grow, MFA is an essential tool for safeguarding accounts and sensitive information.




