In today’s digital world, malware is evolving faster than ever. New viruses, trojans, ransomware, spyware, and other threats appear every single day. Many of them are designed to bypass traditional antivirus systems, making detection and prevention much harder than it used to be.
This is where heuristic analysis becomes extremely important.
Unlike old-school security methods that depend only on recognizing already-known viruses, heuristic-based approaches help detect unknown and newly modified malware by analyzing suspicious patterns and behaviors. This guide will explain heuristic analysis meaning, how it works, why it matters, and how it fits into modern cybersecurity.
If you’ve been hearing terms like heuristic scanning, heuristic detection, or heuristic based detection and want a clear and detailed explanation, you’re in the right place.
What is the Heuristic Analysis Meaning
Let’s begin with the basics.
Heuristic analysis meaning (simple explanation)
Heuristic analysis is a method of detecting malware by examining code or program behavior for suspicious characteristics instead of relying only on known malware signatures.
In other words, instead of asking:
“Have we seen this virus before?”
Heuristic analysis asks:
“Does this program behave like a virus or look suspicious, even if it’s new?”
This technique is extremely valuable today because attackers continuously create:
- Brand-new viruses that have never been recorded
- Modified versions of old malware (slight edits to bypass detection)
- Polymorphic malware that changes itself regularly
That is why heuristic analysis is one of the most powerful tools in modern antivirus and security systems.
Why Traditional Virus Detection Isn’t Enough Today
Before we go deeper into heuristic scanning, it’s important to understand how traditional antivirus detection works and why it has limitations.
Traditional Virus Detection vs Heuristic Analysis
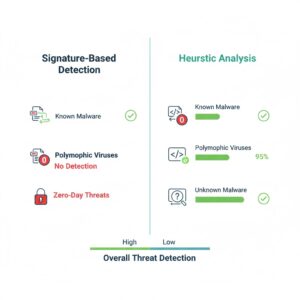
What is Signature-Based Detection?
Signature-based detection is one of the oldest and most widely used methods of malware detection.
It works like this:
- Security researchers analyze malware samples
- They extract a unique “signature” (digital fingerprint) from the malicious code
- That signature is stored in an antivirus database
- When your antivirus scans files, it compares them against the signature database
- If the file matches a known signature, it gets flagged and blocked
This method is accurate when the malware is already known.
Why Signature Detection Has Limitations
Signature detection is still useful, but it has a major weakness:
It struggles with unknown threats.
Cybercriminals are extremely creative, and they know that signature detection depends on previously discovered samples. So attackers constantly create new versions of malware that look slightly different in code but behave the same.
Some reasons signature detection fails include:
- Zero-day malware
A new virus that has never been seen before won’t have a signature. - Modified malware variants
Attackers change small pieces of code so the virus becomes “new” to signature scanners. - Massive volume of threats
Tens of thousands of suspicious files can emerge daily, and not all can be analyzed instantly. - Polymorphic and metamorphic malware
These threats change their code automatically, making signatures unreliable.
This is exactly why heuristic based detection became essential in modern cybersecurity.
Why Heuristic Analysis Is Needed
Signature-based methods are reactive—they work best after malware is known.
But today, cybersecurity demands proactive protection.
Heuristic analysis provides that proactive layer by detecting threats based on suspicious indicators rather than waiting for a signature update.
This means:
- Faster detection of emerging malware
- Better protection from never-before-seen threats
- Stronger defense against constantly changing viruses
What Threats Can Heuristic Analysis Detect?
The biggest advantage of heuristic analysis is its ability to identify threats beyond the signature database.
Heuristic methods can detect:
New and Unknown Malware
Even if the malware has never been recorded, heuristic systems can identify suspicious behavior and code patterns.
Modified Malware Variants
If a known virus is edited slightly, signature detection might miss it. But heuristic detection may still catch it because the malware’s behavior remains suspicious.
Polymorphic Viruses
Polymorphic malware is a type of threat that changes its structure frequently to avoid detection. Since heuristic scanning focuses on behavior and suspicious patterns, it becomes one of the few effective methods against this kind of malware.
Suspicious Applications and Scripts
Heuristics can also detect suspicious scripts, macros, or executables that may not yet be classified as malware but behave in risky ways.
How Does Heuristic Analysis Work?
Now let’s get into the most important part: how heuristic analysis actually works behind the scenes.
Heuristic detection is done mainly using two methods:
- Static heuristic analysis
- Dynamic heuristic analysis
Both are powerful, and many modern security tools combine them.
Static Heuristic Analysis (Code-Based Inspection)
What is Static Heuristic Analysis?
Static heuristic analysis is when a program is examined without running it.
This usually involves:
- Extracting or decompiling parts of the program code
- Analyzing instructions and structure
- Comparing it with known suspicious patterns stored in heuristic rules or databases
Think of it like reading a recipe before cooking it and realizing it contains dangerous ingredients.
How Static Heuristic Scanning Works Step-by-Step
A typical static heuristic scanning process includes:
Code Decompilation or Extraction
Security tools may unpack or break down the file into parts that can be analyzed.
Pattern Recognition
The scanner looks for suspicious traits such as:
- Obfuscated code (hidden or scrambled instructions)
- Strange imports or APIs commonly used by malware
- Attempts to modify system files
- Hard-coded suspicious URLs or IP addresses
- Packed executables used to hide malware
Similarity Matching
The code may be compared against previously flagged suspicious code patterns.
If the match crosses a certain threshold, it may be flagged.
Advantages of Static Heuristic Detection
Static heuristics are beneficial because:
- They can detect suspicious files quickly
- They don’t need to execute the malware
- They work well in early-stage scanning and email attachments filtering
Limitations of Static Heuristic Analysis
Static analysis also has drawbacks:
- Some malware hides itself well through encryption or packing
- It might miss threats that only show malicious behavior when executed
- Advanced malware may appear clean until run
That’s why dynamic heuristic analysis is also used.
Dynamic Heuristic Analysis (Behavior-Based Inspection)
What is Dynamic Heuristic Analysis?
Dynamic heuristics involve running the suspicious file in a safe, controlled environment and monitoring its behavior.
This environment is usually called:
- A sandbox
- A virtual machine
- An isolated testing container
This method is like placing a suspicious object in a lab and observing what it does before allowing it into the
Also Read: What Is a Drive by Download?
How Dynamic Heuristic Analysis Works
Dynamic heuristic detection generally follows this process:
File Isolation
The suspicious file is placed inside a sandbox environment where it cannot harm the real system.
Execution Simulation
The system “runs” the file to observe how it behaves.
Behavior Monitoring
The security tool watches for malware-like activities such as:
- Self-replication (copying itself into other folders)
- Creating hidden files
- Editing registry settings
- Modifying system startup programs
- Disabling security software
- Encrypting files (common in ransomware)
- Injecting code into other processes
- Attempting to connect to suspicious external servers
- Downloading additional payloads
Threat Decision
If the actions match malicious behavior rules, the file is flagged and blocked.
Why Dynamic Heuristic Scanning is So Effective
Dynamic heuristics are powerful because malware can’t “hide” its actions when it executes.
Even if the code looks clean in static scanning, behavior-based detection can still catch it if it acts like malware.
This makes dynamic heuristics extremely useful against:
- Zero-day threats
- Fileless malware
- Script-based attacks
- Polymorphic viruses
Benefits of Heuristic Analysis in Cybersecurity
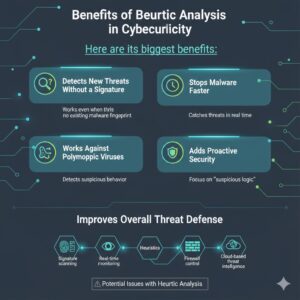
Heuristic analysis plays a key role in modern security strategies. Here are its biggest benefits:
Detects New Threats Without a Signature
This is the number one reason heuristic based detection is valuable. It works even when there is no existing malware fingerprint.
Stops Malware Faster
Instead of waiting for security researchers to identify and add signatures, heuristic detection catches threats in real time.
Works Against Polymorphic Viruses
Since polymorphic malware constantly changes its code, signature detection may fail. Heuristic scanning has a higher chance to detect it by suspicious behavior.
Adds Proactive Security
Heuristic analysis strengthens security systems by focusing on “suspicious logic” rather than only known malware files.
Improves Overall Threat Defense
Modern antivirus solutions don’t rely on one technique. Heuristics strengthen security when combined with:
- Signature scanning
- Real-time monitoring
- Firewall control
- Cloud-based threat intelligence
Potential Issues with Heuristic Analysis
Although heuristic analysis is extremely useful, it also comes with challenges.
False Positives
A false positive happens when a harmless file is incorrectly flagged as malware.
This can happen because heuristic scanning is based on probability and suspicious behavior rules. Sometimes legitimate software does things that look suspicious, such as:
- Modifying system files during installation
- Changing registry settings
- Updating background processes automatically
To reduce this risk, heuristics must be properly calibrated and continuously improved.
Requires Careful Tuning
If heuristic sensitivity is too high:
- You get many false positives
- Legitimate apps may be blocked
If heuristic sensitivity is too low:
- Some new threats might slip through
That’s why security companies often run heuristic scanning as one layer of multiple protections.
Performance Impact
Dynamic analysis, especially sandboxing, may require more system resources and time compared to simple signature scanning. However, with modern cloud-powered and optimized systems, this problem is becoming less noticeable for most users.
Heuristic Analysis in Modern Antivirus Solutions
In real-world security systems, heuristic analysis is usually not used alone. Instead, it works as part of a multi-layer defense system.
A strong cybersecurity setup may include:
Signature-Based Detection
Catches known malware accurately.
Heuristic Detection
Catches unknown threats and suspicious variants.
Behavior Monitoring
Continuously checks system activity even after installation.
Web Protection
Blocks malicious sites, phishing links, and unsafe downloads.
Ransomware Protection
Prevents unauthorized encryption of files.
Email Scanning
Filters suspicious attachments and phishing attempts.
This combination creates a far more reliable defense than any single method.
Why Businesses and Individuals Need Heuristic Scanning
Heuristic scanning is not just for cybersecurity experts—it benefits everyone.
For Individuals
Heuristic analysis protects users from:
- Fake cracked software downloads
- Email attachment malware
- Malicious browser extensions
- Trojans hiding in free apps
For Businesses
Companies benefit even more because they face:
- Targeted ransomware attacks
- Insider threats
- Malware designed specifically for corporate networks
- Phishing campaigns aimed at employees
In such cases, heuristic based detection can stop threats before they spread through the organization.
Best Practices to Support Heuristic Protection
Even though heuristic analysis is powerful, you should combine it with smart safety habits:
- Avoid downloading software from unknown sources
- Don’t click suspicious links in emails
- Keep operating system and apps updated
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication
- Backup important data regularly
- Enable real-time protection and firewall settings
Cybersecurity is always strongest when technology and smart behavior work together.
Conclusion
Cyber threats are increasing in volume and sophistication every year. Traditional signature-based antivirus detection is still useful, but it cannot handle modern malware alone—especially zero-day threats, modified variants, and polymorphic viruses.
That’s why heuristic analysis has become one of the most essential cybersecurity techniques today.
By using heuristic scanning methods such as static and dynamic heuristics, security tools can identify suspicious behavior, detect unknown malware early, and protect systems before damage occurs.
If you truly want strong protection in today’s digital environment, understanding the heuristic analysis meaning and the power of heuristic detection is a big step toward safer online activity.
FAQs
What is heuristic analysis in antivirus software?
Heuristic analysis is a malware detection method that identifies suspicious code patterns or behaviors to detect threats, even if the malware is new and does not have a signature in the database.
What is heuristic scanning?
Heuristic scanning is the process of checking files and programs using heuristic rules to detect suspicious characteristics that indicate possible malware infection.
What is the difference between signature detection and heuristic detection?
Signature detection finds malware by matching known virus fingerprints, while heuristic detection identifies new or modified malware by analyzing suspicious patterns and behaviors.
Can heuristic analysis detect polymorphic viruses?
Yes. Heuristic analysis is one of the few effective methods against polymorphic viruses because it focuses on behavior and suspicious traits rather than fixed signatures.
What is heuristic based detection?
Heuristic based detection is a proactive approach to identifying malware using suspicion-based rules and behavior analysis, rather than relying only on known virus signatures.
Why does heuristic analysis sometimes give false positives?
False positives happen when safe software behaves like malware, such as editing system files or running background processes. Heuristic systems must be tuned carefully to minimize this.
Is heuristic scanning enough for full protection?
Heuristic scanning is powerful, but best security comes from combining it with signature detection, behavioral monitoring, safe browsing practices, and regular updates.




