In the past few years, one digital trend has caught the attention of artists, investors, and tech enthusiasts worldwide — NFTs. But what are NFTs, and how do they work? Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have revolutionized the concept of ownership in the digital age. From digital art and collectibles to music and gaming, NFTs have created a new ecosystem where digital assets can be owned, traded, and authenticated just like physical goods.
Although the underlying blockchain technology has existed for years, NFTs rose to prominence in 2020 and 2021, particularly within the art world. They have since expanded far beyond that, becoming a crucial part of the growing Web3 economy. However, while NFTs have opened new doors for creators and investors, they have also drawn criticism for their volatility, speculation, and exposure to scams.
In this detailed guide, we will explore what NFTs are, how they work, how to buy them, where to trade them, their benefits and risks, and how to protect yourself in this fast-moving digital marketplace.
NFT Meaning and Definition
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token. To understand what that means, let’s break it down.
The word fungible refers to something that is interchangeable. For example, a ten-dollar bill or a Bitcoin can be exchanged for another of the same value — they are identical in worth and nature. By contrast, non-fungible means something unique and irreplaceable. A rare painting like the Mona Lisa, for instance, is non-fungible because there is only one original version in existence.
NFTs apply this same concept to the digital world. An NFT is a unique digital asset verified and stored on a blockchain, making it impossible to duplicate or counterfeit. Each NFT contains a distinct identification code and metadata that distinguishes it from other tokens.
NFTs can take many forms — digital art, videos, music, GIFs, memes, trading cards, in-game items, and even virtual real estate. Each one represents ownership of a specific item or piece of content. Unlike regular files that can be endlessly copied, the blockchain ensures that each NFT is verifiably one of a kind.
How Do NFTs Work?
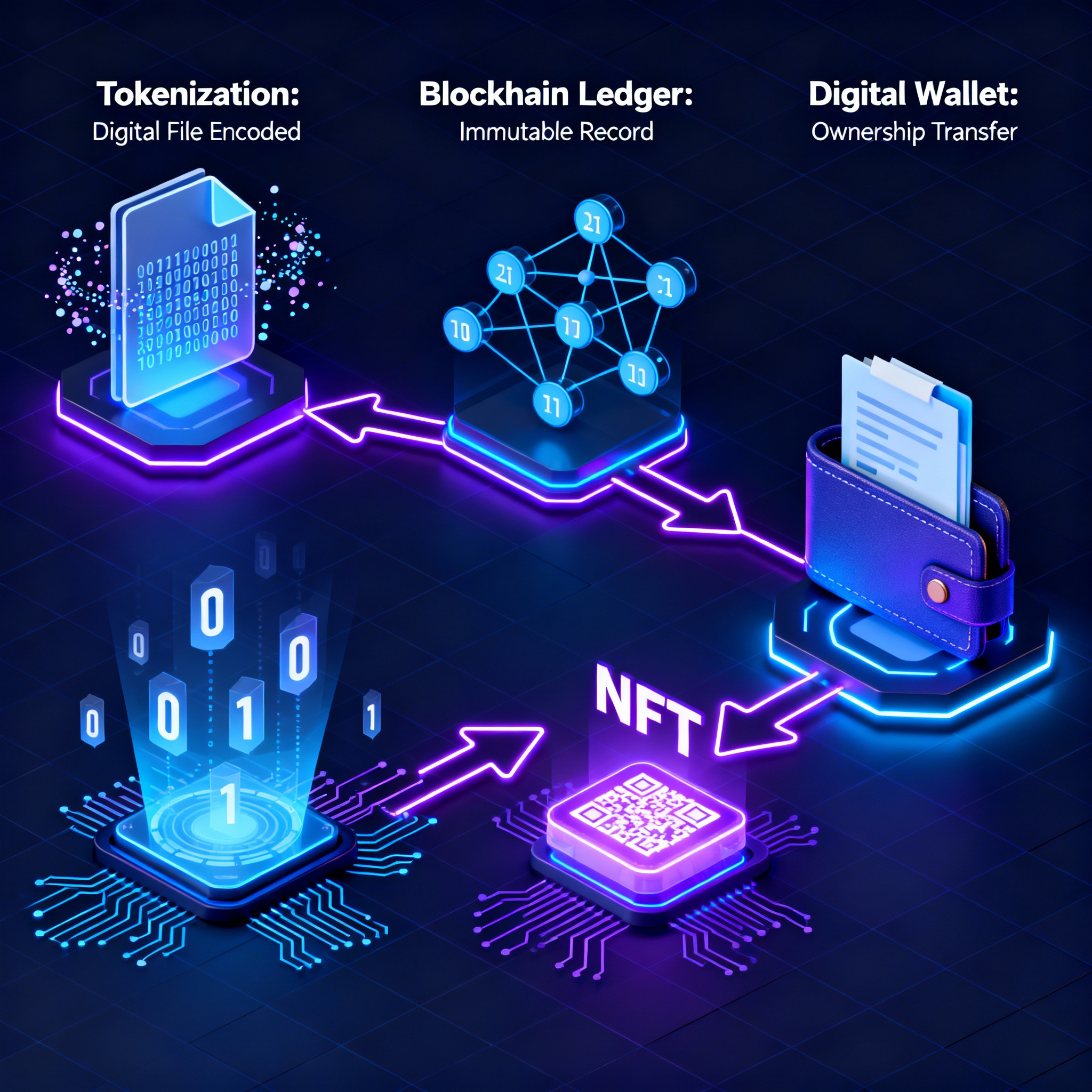
To understand how NFTs work, you first need to know what a blockchain is. A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This means that every NFT’s ownership history, sale, and authenticity can be transparently verified by anyone.
When a digital file is converted into an NFT, it undergoes a process called minting. During minting, the file is added to the blockchain, given a unique code, and linked to the creator’s digital wallet. Once minted, that NFT exists as a distinct token on the blockchain, proving its authenticity and ownership.
Each NFT is stored on the blockchain as a record containing the following information:
- The identity of the creator
- The current owner
- A unique identifier or token ID
- Metadata (such as the title, description, and file link)
Because blockchain networks like Ethereum are public, anyone can verify an NFT’s transaction history. This transparency helps eliminate fraud and duplication, as every sale or transfer is recorded permanently.
NFTs derive their value from scarcity, authenticity, and demand. Just like physical collectibles, their worth can fluctuate based on popularity, creator reputation, and rarity. Some NFTs have sold for millions, while others are valued at just a few dollars.
Moreover, NFTs are not limited to digital art. They can represent real-world assets, such as property deeds, concert tickets, or certificates, making buying and selling more efficient and reducing the chances of fraud.
How to Buy NFTs
Buying NFTs involves several steps. While the process may sound complicated at first, it becomes simple once you understand the basics of cryptocurrency and blockchain transactions.
Open a Crypto Exchange Account
The first step in buying NFTs is to open an account on a crypto exchange — a platform where you can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies. Popular options include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken.
Since most NFTs are built on the Ethereum blockchain, you’ll need to purchase Ethereum (ETH), the cryptocurrency used for NFT transactions.
Open a Crypto Wallet
A crypto wallet is a digital tool that stores your cryptocurrencies and NFTs securely. It provides access to your blockchain assets through a private key. You’ll also receive a seed phrase, which acts as a recovery key to access your wallet if you lose access to your account.
There are two main types of wallets:
- Hot wallets: Connected to the internet and accessible via mobile apps or browser extensions. These are convenient but more vulnerable to hacking. Examples include MetaMask and Trust Wallet.
- Cold wallets: Physical hardware wallets not connected to the internet, offering greater security. Examples include Ledger Nano and Trezor.
When choosing a wallet, ensure it is compatible with Ethereum, since most NFTs are traded on that blockchain.
Transfer Ethereum into Your Wallet
Once you’ve purchased ETH from your exchange, you need to transfer it to your wallet. This ETH will be used to buy NFTs or pay transaction fees, known as gas fees.
Connect Your Wallet to an NFT Marketplace
Next, connect your crypto wallet to an NFT marketplace. The connection allows you to make purchases directly using your wallet balance.
Buy NFTs
Once connected, you can start exploring collections, bidding in auctions, or buying NFTs directly. When you buy an NFT, the ownership is recorded on the blockchain, and the token is transferred to your wallet. However, buying an NFT gives you ownership rights — not necessarily copyright or reproduction rights — unless explicitly stated by the creator.
Also Read: What is Tor Browser and is it safe?
What is an NFT Marketplace?
An NFT marketplace is an online platform where NFTs are created, bought, sold, or traded. These platforms act as the digital equivalent of art galleries or stock exchanges for digital assets.
NFT marketplaces typically fall into three categories:
Open Marketplaces
These are platforms where anyone can mint, buy, or sell NFTs. They provide the largest range of assets but also carry a higher risk of counterfeit works. OpenSea is the best-known open marketplace, featuring millions of NFTs across art, music, fashion, gaming, and collectibles.
Closed Marketplaces
Closed marketplaces are more selective. Only approved artists or creators can list NFTs, ensuring higher quality and authenticity. Examples include SuperRare and Foundation.
Proprietary Marketplaces
These are operated by specific companies selling their own branded NFTs. For example, NBA Top Shot sells officially licensed basketball highlight clips. Proprietary marketplaces typically focus on one niche or brand.
Each marketplace has its own fee structure and verification process. Some even allow users to create new NFTs directly on the platform through a process called minting.
Examples of NFT Marketplaces
While hundreds of NFT marketplaces exist, a few have become major players in the space:
- OpenSea: The largest NFT marketplace in the world, offering a wide variety of NFTs across categories such as art, music, and virtual real estate.
- NBA Top Shot: Specializes in sports collectibles, allowing fans to own officially licensed basketball highlights.
- Nifty Gateway: Focuses on digital art and features well-known artists and brands.
- Rarible: A decentralized platform that lets users create, buy, and sell NFTs using Ethereum.
These marketplaces make it easy for users to buy, sell, and trade NFTs, but it’s important to use verified and trusted platforms to avoid scams.
NFT Scams and How to Avoid Them
While NFTs offer innovative opportunities, they have also become targets for fraud. The market’s rapid growth has led to numerous NFT scams, so understanding how to identify and avoid them is crucial.
Common NFT Scams
- Phishing scams: Scammers use fake links or pop-ups to steal wallet credentials.
- Catfishing: Fraudsters create fake websites or social media accounts pretending to be popular NFT creators.
- Counterfeit NFTs: Scammers sell plagiarized digital art as original works.
- Pump-and-dump schemes: Scammers artificially inflate NFT prices to sell at a profit, leaving buyers with worthless assets.
- Free mint scams: Fake NFT minting events where users unknowingly grant scammers control over their wallets.
How to Stay Safe
- Always use strong passwords and two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Store crypto in a cold wallet instead of leaving it on an exchange.
- Avoid clicking suspicious links or responding to unknown direct messages.
- Conduct research before purchasing — verify the creator’s authenticity.
- Make small test transactions before investing large amounts.
- Ignore strange NFTs sent to your wallet, as they might contain malicious code.
By following these safety practices, you can protect your assets and minimize the risk of falling victim to scams.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NFTs
Like any innovation, NFTs have both benefits and downsides.
Advantages
- Digital ownership: NFTs allow users to own digital assets verifiably.
- Creator empowerment: Artists can sell directly to buyers without intermediaries, earning royalties from future resales.
- Transparency: Every transaction is permanently recorded on the blockchain.
- Global access: Anyone with internet access can buy or sell NFTs.
- Tokenization of real assets: NFTs can represent real-world items like real estate or event tickets, improving efficiency and reducing fraud.
Disadvantages
- Market volatility: NFT prices can rise and fall dramatically in short periods.
- Scams and fraud: Lack of regulation makes it easier for bad actors to exploit users.
- Environmental impact: Some blockchains, like Ethereum, have been criticized for high energy use (though newer versions are more sustainable).
- Copyright issues: Buying an NFT doesn’t always grant reproduction rights.
- Uncertain value: NFTs can lose relevance if public interest declines.
FAQs
What does NFT stand for?
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token. It represents unique digital assets that cannot be exchanged for identical items due to their distinct characteristics.
What is an example of an NFT?
Examples of NFTs include digital artwork, trading cards, music albums, sports highlights, memes, and even tweets. For example, Twitter founder Jack Dorsey sold his first tweet as an NFT in 2021.
Are NFTs cryptocurrency?
No, NFTs and cryptocurrencies are different. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum are fungible, meaning one unit is equal to another. NFTs are non-fungible, each with its unique value and identity.
What are NFTs used for?
NFTs represent ownership of unique items, including art, music, videos, and collectibles. They are stored on blockchains like Ethereum, ensuring authenticity and secure ownership.
What is NFT art?
NFT art refers to digital artwork that is tokenized and stored on the blockchain. It certifies originality, ownership, and provenance, making digital art collectible and tradable.
Are NFTs a good investment?
NFTs can be profitable but are highly speculative. Their value depends on rarity, creator reputation, and market demand, so buyers should invest cautiously.
Can NFTs be copied?
The image or file can be copied, but the ownership token on the blockchain cannot be duplicated. The blockchain entry is what proves ownership.
Conclusion
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, have transformed how we think about digital ownership. They allow artists, creators, and collectors to authenticate and trade unique digital items on a secure blockchain. Understanding what NFTs are and how they work is essential before diving into the market, as it combines creativity, technology, and investment in one ecosystem.
While NFTs present exciting opportunities, they also come with risks — from scams to market volatility. For anyone interested in exploring this space, research and caution are key. NFTs may still be evolving, but their impact on digital ownership and innovation is undeniable.
In the years ahead, as blockchain technology matures and regulations strengthen, NFTs are likely to play an even greater role in art, gaming, entertainment, and beyond. Whether you’re an artist, investor, or tech enthusiast, understanding NFTs is your first step into the future of digital assets.




