In today’s interconnected world, every click, post, and online interaction leaves behind a trail known as your digital footprint. Understanding what a digital footprint is and why it matters is crucial to managing your online identity, protecting your privacy, and safeguarding your personal information. This blog will guide you through the concept, types, risks, and management strategies of digital footprints.
What is a Digital Footprint?
A digital footprint, sometimes called a digital shadow or electronic footprint, refers to the trail of data you leave when using the internet. It encompasses your online activities such as social media posts, emails, website visits, purchases, and even data collected automatically by websites and apps. This footprint shapes your digital identity and can be used to track your online behavior.
Types of Digital Footprints
Active Digital Footprints

An active digital footprint consists of the information you intentionally share online. This includes:
- Posting on social media
- Filling out online forms
- Sending emails
- Writing blog posts
- Making online purchases
- Participating in forums
These actions are deliberate and usually visible to others, giving you some control over this part of your footprint.
Passive Digital Footprints
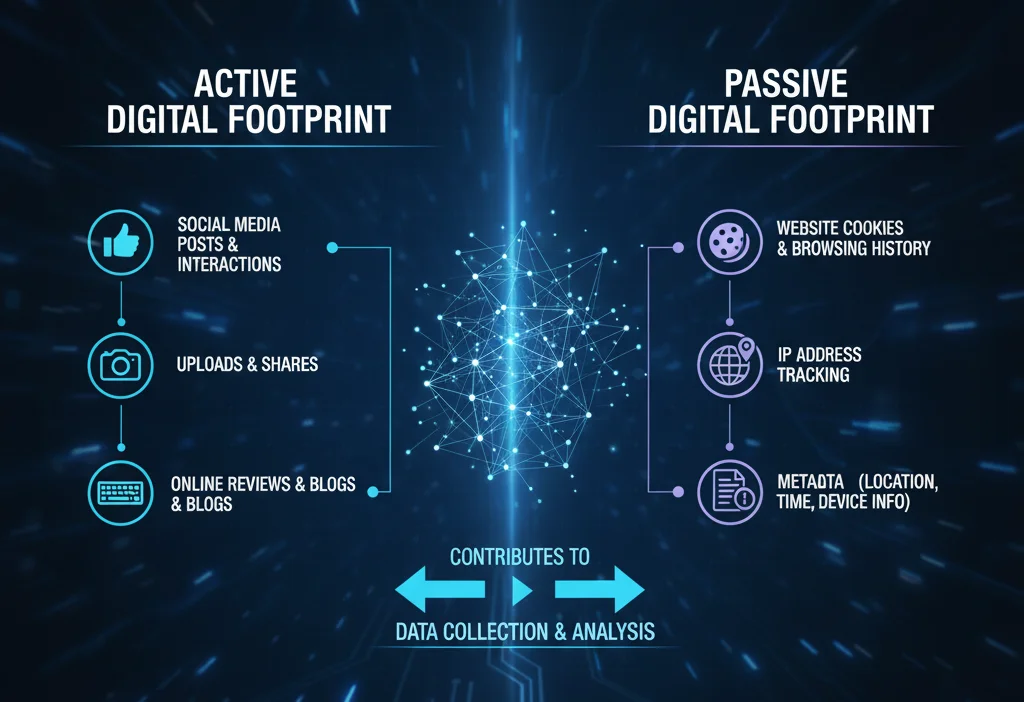
Passive digital footprints are created without your explicit knowledge. This data is collected automatically by websites, apps, and other digital services as you browse, such as through:
- Cookies
- IP address tracking
- Metadata in files
- Location data
- Analytics tools
Since this happens behind the scenes, it is less visible and harder to control.
Also Read: What Are Biometric Applications? Types, Examples, and Use Cases
Types of Data in Your Digital Footprint
Your digital footprint is made up of various types of data:
- Personal Information: Name, contact details, date of birth, address, phone numbers, and financial information.
- Behavioral Data: Browsing habits, search queries, website visit patterns, and preferences.
- Transactional Data: Online purchases, payment methods, banking activities, and subscription records.
- Location Data: GPS coordinates, IP-based location tracking, and app-collected location information.
- Metadata: Background details in digital files, such as timestamps, device info, and file creation dates.
How Digital Footprints Are Created
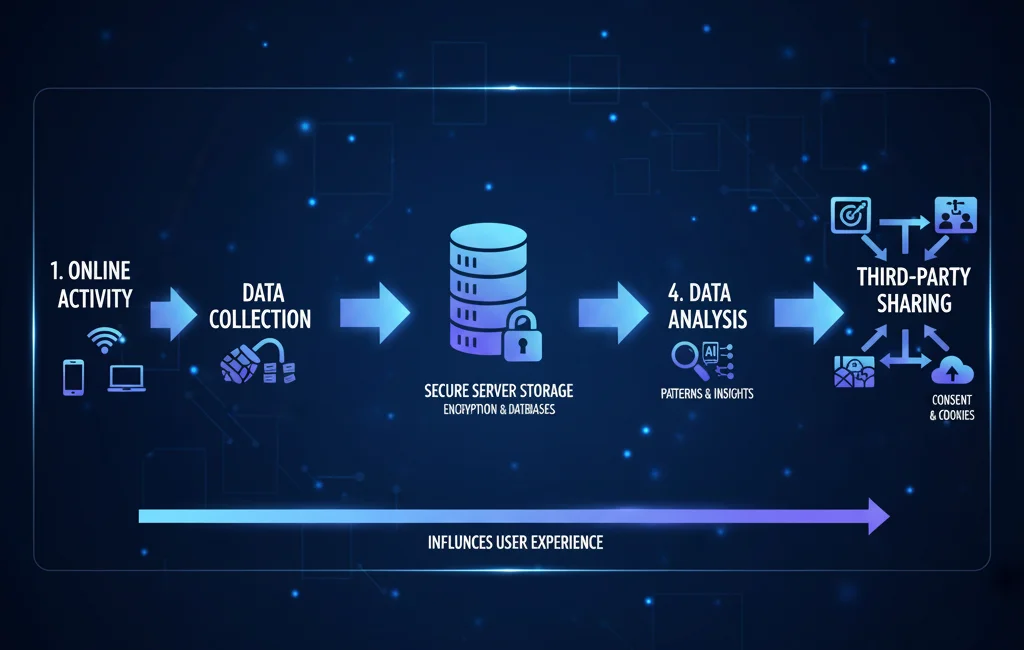
Every interaction with digital platforms contributes to your footprint:
- You engage with websites or mobile apps.
- Data is collected through cookies, forms, and analytic tools.
- The collected data is stored on servers or in the cloud.
- Data is analyzed for patterns and sometimes shared with third parties like advertisers or government agencies.
Why Digital Footprints Matter

For Individuals
Your digital footprint influences your:
- Online reputation
- Privacy and security
- Job prospects
- Relationships
A poorly managed footprint may expose you to identity theft, phishing, or unwanted tracking.
For Businesses
Companies use digital footprints to:
- Understand customer behavior
- Personalize marketing
- Improve services
- Detect fraud
- Optimize operations
For Society
Digital footprints raise broader issues such as:
- Digital equity
- Environmental impact (digital carbon footprint)
- Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA
Risks and Concerns
- Security Risks: Identity theft, phishing, account compromise.
- Privacy Concerns: Unauthorized data sharing, location tracking.
- Reputational Risks: Misinterpretation or viral spread of content.
- Financial Risks: Fraudulent transactions, unauthorized use.
Managing Your Digital Footprint
Audit Your Online Presence
- Search your name online.
- Review social media accounts.
- Monitor where your data appears.
Secure Your Accounts
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Update security settings regularly.
Control What You Share
- Be cautious with online posts and personal info.
- Adjust privacy settings.
- Review terms of service and privacy policies.
Use Privacy Tools
- Leverage browser privacy settings.
- Disable unnecessary location services.
- Use VPNs and encrypted communication tools.
Clean Up Your Footprint
- Delete old posts and unused accounts.
- Request data deletion where possible.
- Exercise your right to be forgotten.
Monitor Continuously
- Set up alerts for your name.
- Regularly review online activity.
- Stay informed about data breaches.
The Role of Biometrics in Digital Footprint Management
Biometric methods like fingerprint scanning and facial recognition enhance security by:
- Ensuring account access reflects your unique identity.
- Preventing fraud and reducing fake accounts.
- Improving identity verification processes.
Best Practices for Digital Footprint Management
- Be aware of your sharing habits.
- Conduct regular privacy audits.
- Adopt strong security measures.
- Make informed privacy choices.
- Stay updated on digital trends and laws.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
- AI and machine learning improve pattern recognition and fraud detection.
- IoT devices add sensor data footprints.
- Data protection laws continue evolving, shaping footprint management.
Conclusion
Your digital footprint shapes your online identity and activities. Managing it protects your privacy, security, and reputation while allowing you to benefit from digital opportunities. By understanding your footprint, controlling your data, and leveraging security tools like biometrics, you can confidently navigate the digital world.
Take charge of your digital footprint today to build a safer, more trustworthy online presence.




