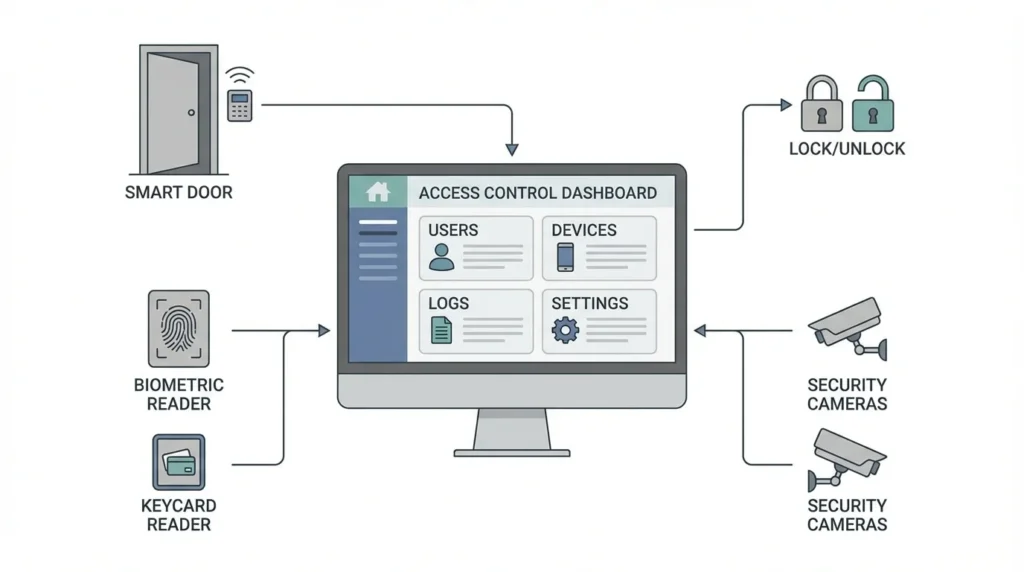
A door access control system is a modern security solution that helps control who can enter or exit a specific door, room, or building. Instead of using traditional keys, access is granted through digital methods such as cards, PINs, biometrics, or mobile devices. These systems are widely used in offices, residential buildings, hospitals, factories, and institutions where security and controlled access are important. Door access control systems not only improve safety but also make access management easier, more flexible, and more reliable.
What Is a Door Access Control System?
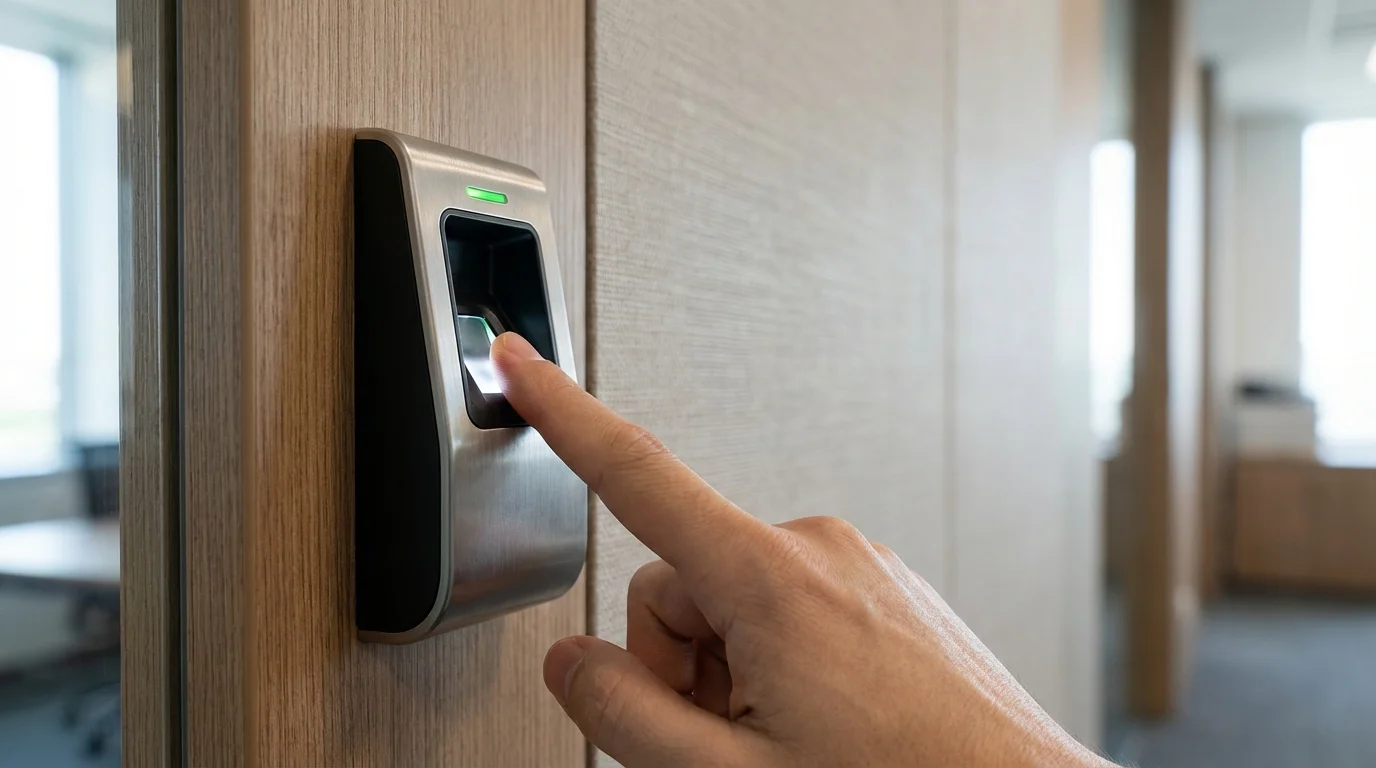

A door access control system is a security system that restricts and manages entry to physical spaces. It allows only authorized individuals to access specific doors at approved times.
These systems work by verifying a user’s identity through credentials like cards, PINs, or biometric data. Once verified, the system sends a signal to unlock the door. If the user is not authorized, access is denied.
Unlike traditional locks that rely on physical keys, access control systems allow permissions to be updated digitally. This means lost cards can be deactivated, access can be time-based, and entry logs can be tracked for better security and accountability.
Key Components of a Door Access Control System
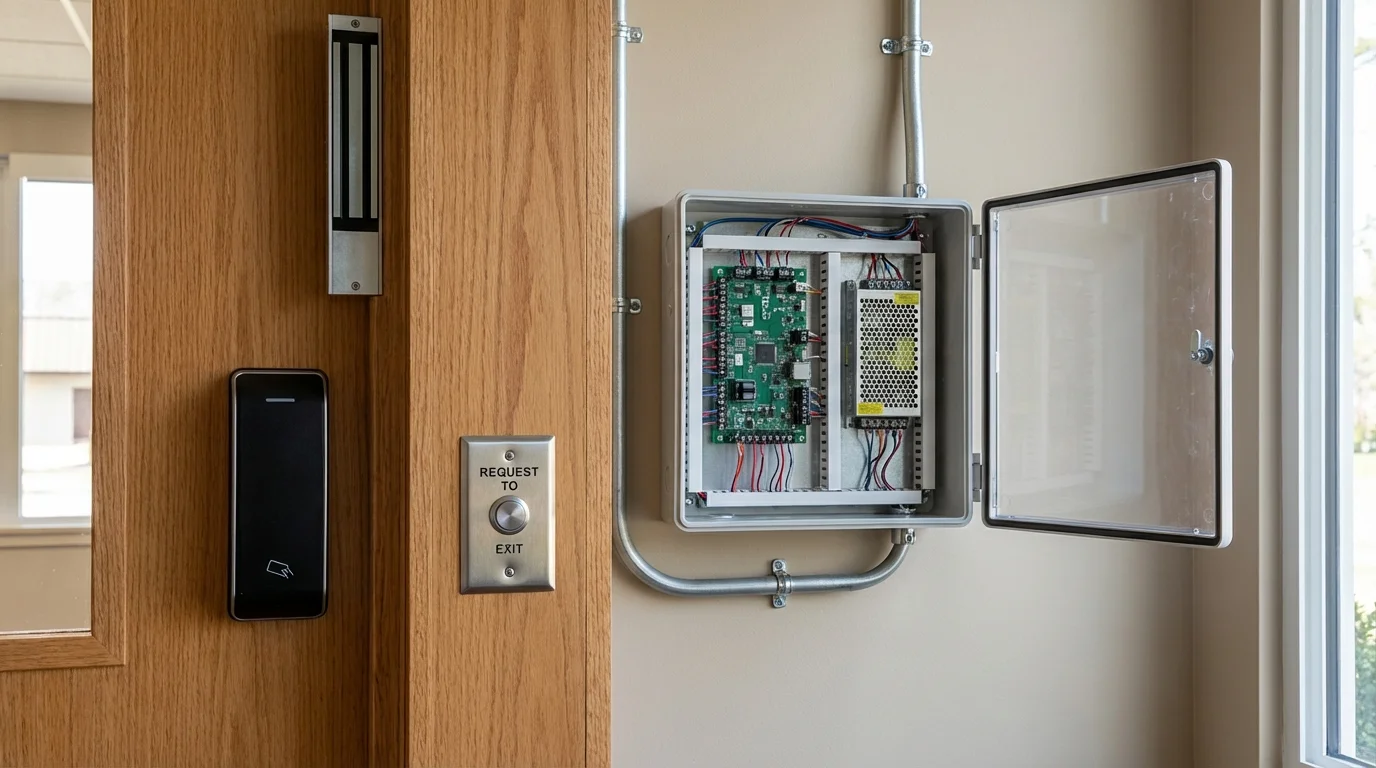
Access Control Panel
The access control panel acts as the brain of the system. It stores access rules and decides whether a person should be allowed entry.
- Maintains a database of users and access rights
- Communicates with door readers and locks
- Sends commands to lock or unlock doors
Door Readers
Door readers are installed near doors to read user credentials and send the data to the control panel for verification.
- Reads cards, PINs, biometric data, or mobile credentials
- Communicates with the control panel in real time or offline
- Acts as the first point of user interaction
Credentials
Credentials are what users present to gain access. They identify and authenticate individuals.
- Cards or key fobs for contactless access
- PIN codes entered via keypads
- Biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition
- Mobile credentials stored on smartphones
Electric Locks
Electric locks physically secure the door and respond to commands from the access control panel.
- Remain locked until access is approved
- Automatically lock after the door closes
- Support different door types and security levels
Power Supply and Backup
Power is essential for access control systems to function reliably.
- Supplies electricity to panels, readers, and locks
- Includes backup batteries for power failures
- Ensures uninterrupted security during outages
Software and Management Platform
Access control software allows administrators to manage and monitor the entire system.
- Create and modify user access permissions
- View access logs and reports
- Monitor door status and system health
Types of Door Access Control Systems

Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
Discretionary Access Control allows system owners or administrators to decide who can access specific doors.
- Access is assigned individually
- Flexible and easy to manage
- Common in small offices and residential buildings
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Mandatory Access Control uses strict rules defined by the system rather than individual users.
- Access is based on security classifications
- Users cannot change permissions
- Used in high-security environments
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control assigns access based on job roles or responsibilities.
- Users inherit access from their role
- Reduces manual access management
- Ideal for growing organizations
Rule-Based Access Control
Rule-Based Access Control grants access based on predefined rules such as time or location.
- Allows time-based or condition-based access
- Enhances security with automation
- Useful for shift-based workplaces
Types of Door Access Control Credentials
Keypads and PIN Codes
Keypads allow users to enter a PIN code to unlock doors.
- Simple and cost-effective
- No physical credential required
- PIN sharing can be a security risk
RFID and Smart Cards
RFID and smart cards are widely used for contactless access.
- Quick and convenient to use
- Easy to replace or deactivate
- Can be lost or stolen if not managed properly
Biometric Access Control
Biometric systems use unique physical characteristics to verify identity.
- High level of security
- Eliminates credential sharing
- Requires proper enrollment and maintenance
Mobile-Based Access Control
Mobile access uses smartphones as digital keys.
- Convenient and modern solution
- Easy credential distribution and revocation
- Depends on phone compatibility and battery
Online vs Offline Door Access Control Systems

Offline Access Control Systems
Offline systems operate without continuous network connectivity.
- Store access data locally
- Suitable for small installations
- Limited reporting and control
Online Access Control Systems
Online systems are connected to a central server or cloud platform.
- Real-time monitoring and control
- Instant updates to access permissions
- Better scalability and reporting
Wired vs Wireless Door Access Control Systems
Wired Access Control Systems
Wired systems use physical cables to connect components.
- Highly reliable communication
- Suitable for permanent installations
- Installation can be complex and time-consuming
Wireless Access Control Systems
Wireless systems use radio or network signals for communication.
- Faster and cleaner installation
- Easy to expand or relocate
- May depend on signal strength and battery life
Benefits of Door Access Control Systems
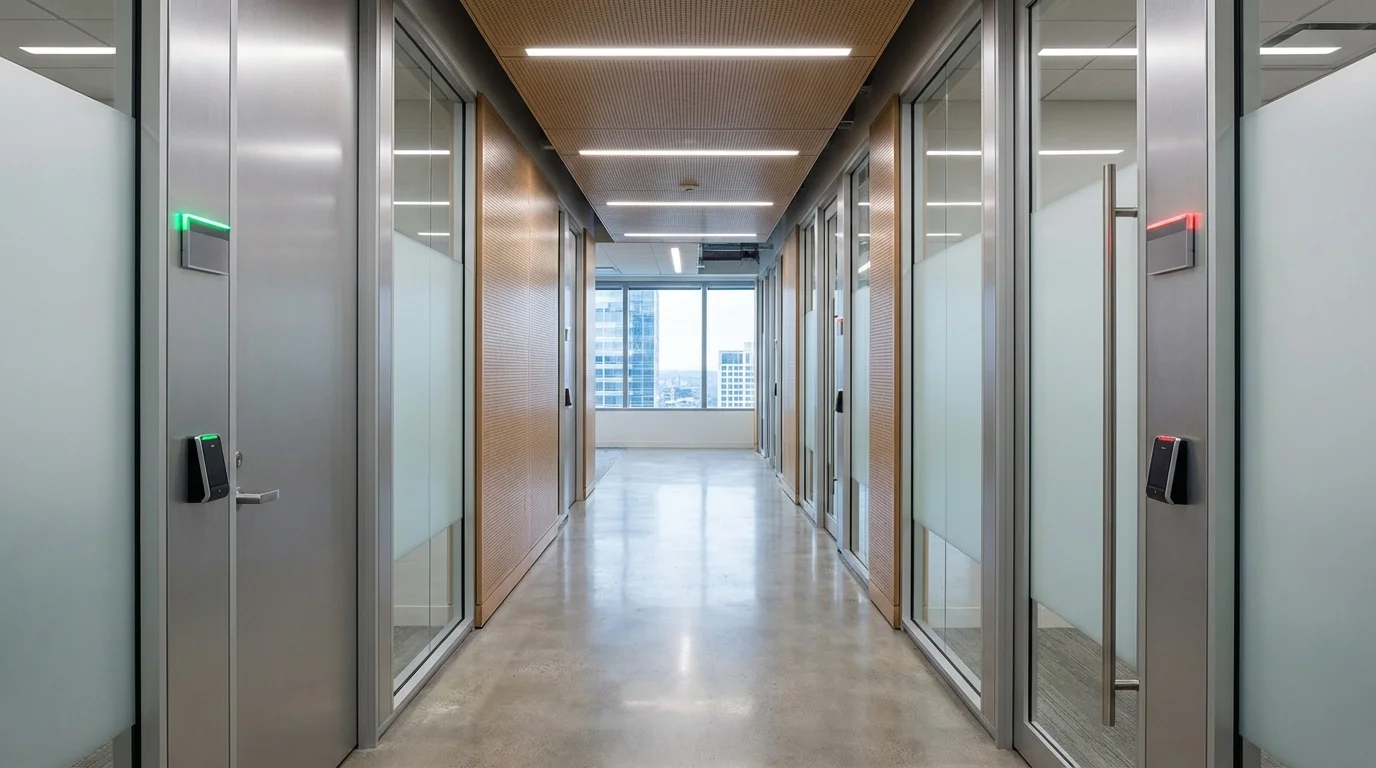

Door access control systems provide both security and operational advantages.
- Improved protection against unauthorized entry
- Detailed tracking of entry and exit activities
- Easy management of users and permissions
- Reduced reliance on physical keys
- Better integration with security infrastructure
Use Cases of Door Access Control Systems
Commercial Buildings
Access control helps manage employee and visitor access efficiently.
- Secures sensitive office areas
- Supports role-based access
- Improves workplace safety
Residential Buildings
Residential access control improves safety and convenience.
- Restricts unauthorized entry
- Supports visitor management
- Enhances resident confidence
Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals require controlled access to protect patients and staff.
- Secures restricted medical areas
- Supports compliance needs
- Limits access to sensitive data zones
Educational Institutions
Schools and colleges use access control for campus safety.
- Manages student and staff access
- Secures laboratories and offices
- Improves overall campus security
Industrial and Manufacturing Units
Factories use access control to protect assets and personnel.
- Restricts access to hazardous zones
- Tracks worker movement
- Supports safety and compliance
Door Access Control System Integration
Access control systems often work best when integrated with other security tools.
- Integration with CCTV for visual verification
- Integration with attendance systems for workforce tracking
- Integration with alarm and fire systems for emergency response
Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Door Access Control System
Selecting the right system requires careful evaluation.
- Level of security required
- Number of doors and users
- Budget and long-term costs
- Ability to scale as needs grow
- Maintenance and support requirements
Common Challenges in Door Access Control Systems
While effective, access control systems can face challenges.
- Power or network interruptions
- Managing large numbers of users
- Lost or misused credentials
- Need for regular system updates
Best Practices for Implementing Door Access Control Systems
Following best practices ensures long-term success.
- Plan access levels carefully
- Review and update permissions regularly
- Use strong authentication methods
- Train users and administrators properly
Conclusion
Door access control systems play a crucial role in modern security by providing controlled, flexible, and trackable access to physical spaces. They offer clear advantages over traditional locking methods and can be customized to meet the needs of different environments. By understanding system components, types, credentials, and best practices, organizations can choose and implement access control solutions that improve safety, efficiency, and peace of mind.
FAQs
What is a door access control system?
A door access control system is a security solution that manages who can enter or exit a door or area. It uses credentials like cards, PINs, biometrics, or mobile devices instead of traditional keys to allow or deny access.
How does a door access control system work?
The system verifies a user’s credential through a door reader. The access control panel checks whether the user has permission and then sends a signal to unlock or keep the door locked.
What are the main types of door access control systems?
The main types include Discretionary Access Control, Mandatory Access Control, Role-Based Access Control, and Rule-Based Access Control. Each type differs in how access permissions are assigned and managed.
Which access control credential is the most secure?
Biometric credentials are considered highly secure because they are based on unique physical traits like fingerprints or facial features, making them difficult to share or duplicate.
Can door access control systems work without the internet?
Yes, offline door access control systems can operate without an internet connection. They store access data locally but offer limited monitoring and reporting features.
What is the difference between wired and wireless access control systems?
Wired systems use physical cables for communication and are highly reliable, while wireless systems use radio or network signals, making them easier to install and expand.
Are door access control systems suitable for small businesses?
Yes, door access control systems can be scaled for small businesses. Simple systems with keypads or cards are cost-effective and easy to manage.
What happens if there is a power failure?
Most door access control systems include backup batteries or power solutions to ensure continued operation during power outages.