In today’s fast-paced digital world, QR codes have become a common sight — whether you’re paying bills, checking restaurant menus, or accessing online information instantly. But with convenience comes risk. Many users often ask — what is the QR code full form, qr code kya hota hai, and more importantly, are QR codes safe to use?
This detailed blog will explain everything you need to know about QR codes — from their meaning and types to potential security threats and safety practices.
QR codes, short for Quick Response codes, have revolutionized the way we interact with digital data. A simple black-and-white square, when scanned, can lead you to a website, connect you to Wi-Fi, or even initiate a payment.
However, the rise in QR code usage has also opened doors for cybercriminals who exploit users’ trust by embedding malicious links in deceptive codes. Understanding QR code security is essential to stay safe while using them daily.
What Are QR Codes?

So, qr code kya hota hai?
A QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that stores information like website links, text, or contact details. Unlike traditional barcodes that store limited data, QR codes can store thousands of characters and are readable both horizontally and vertically.
Whenever you scan a QR code using your smartphone camera or a QR scanner, it decodes the pattern and instantly performs the associated action — such as opening a webpage, displaying text, or adding a contact.
The Origin and Evolution of QR Codes
The QR code full form stands for Quick Response, and it was first developed in 1994 by Denso Wave, a subsidiary of Toyota in Japan. The company wanted a faster and more efficient way to track vehicle parts during manufacturing.
Unlike traditional barcodes, which store information in one direction, QR codes store data in two dimensions — vertically and horizontally — allowing them to hold significantly more data.
The adoption of QR codes began in Japan and later spread worldwide when smartphones began including built-in QR scanners. During the COVID-19 pandemic, their use skyrocketed as contactless solutions became a necessity.
Today, QR codes are used for marketing, payments, verification, authentication, and even digital memorials — truly reflecting their versatility.
How Do QR Codes Work?
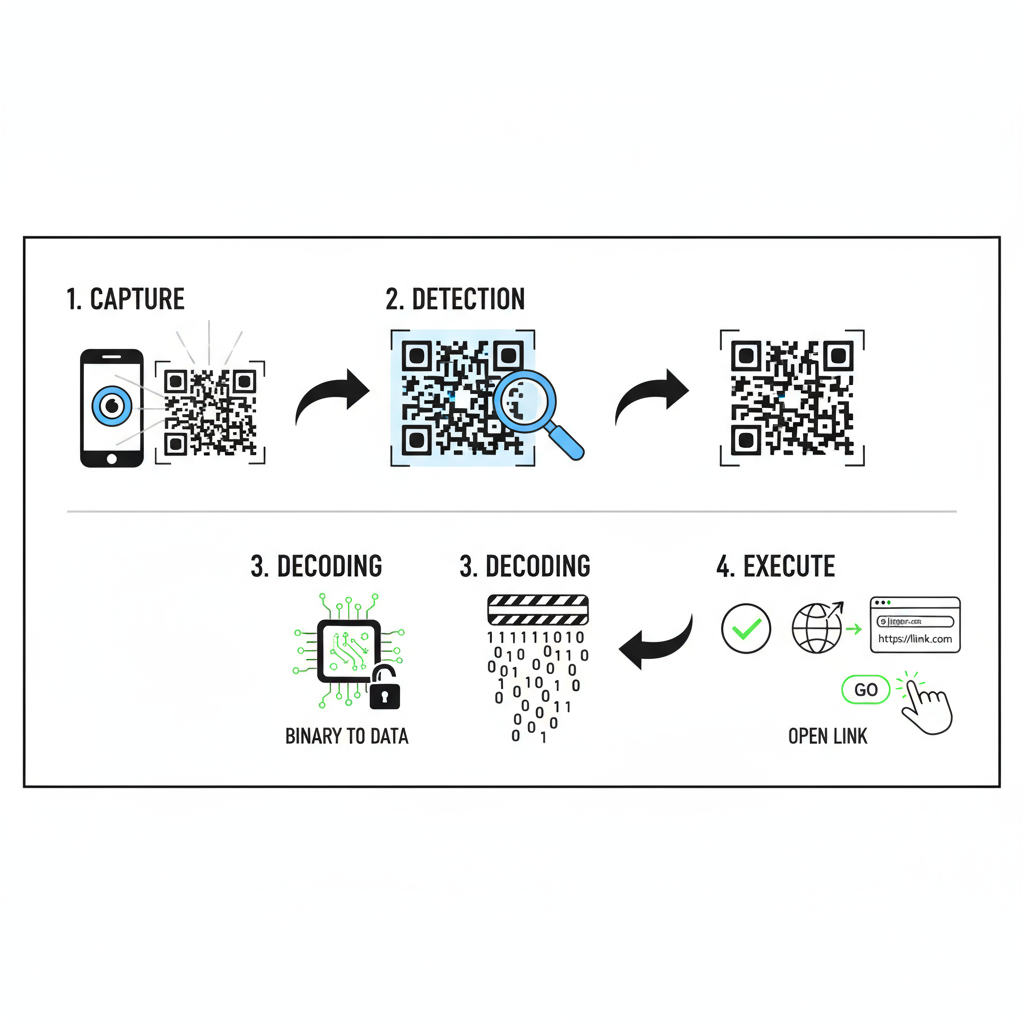
At their core, QR codes work by encoding data into a series of black and white pixels arranged in a square grid. When you scan QR code using your phone’s camera, the scanner detects these patterns and converts them into readable information.
Here’s how it works step by step:
- Scan the QR code using a phone camera or QR reader app.
- The QR reader detects the unique pattern.
- It translates the pattern into binary code (0s and 1s).
- The binary code is converted into meaningful information (text, URL, or data).
Whether you’re scanning for a Wi-Fi password, payment, or login verification, the process remains instant — hence the name “Quick Response.”
The Main Components of a QR Code
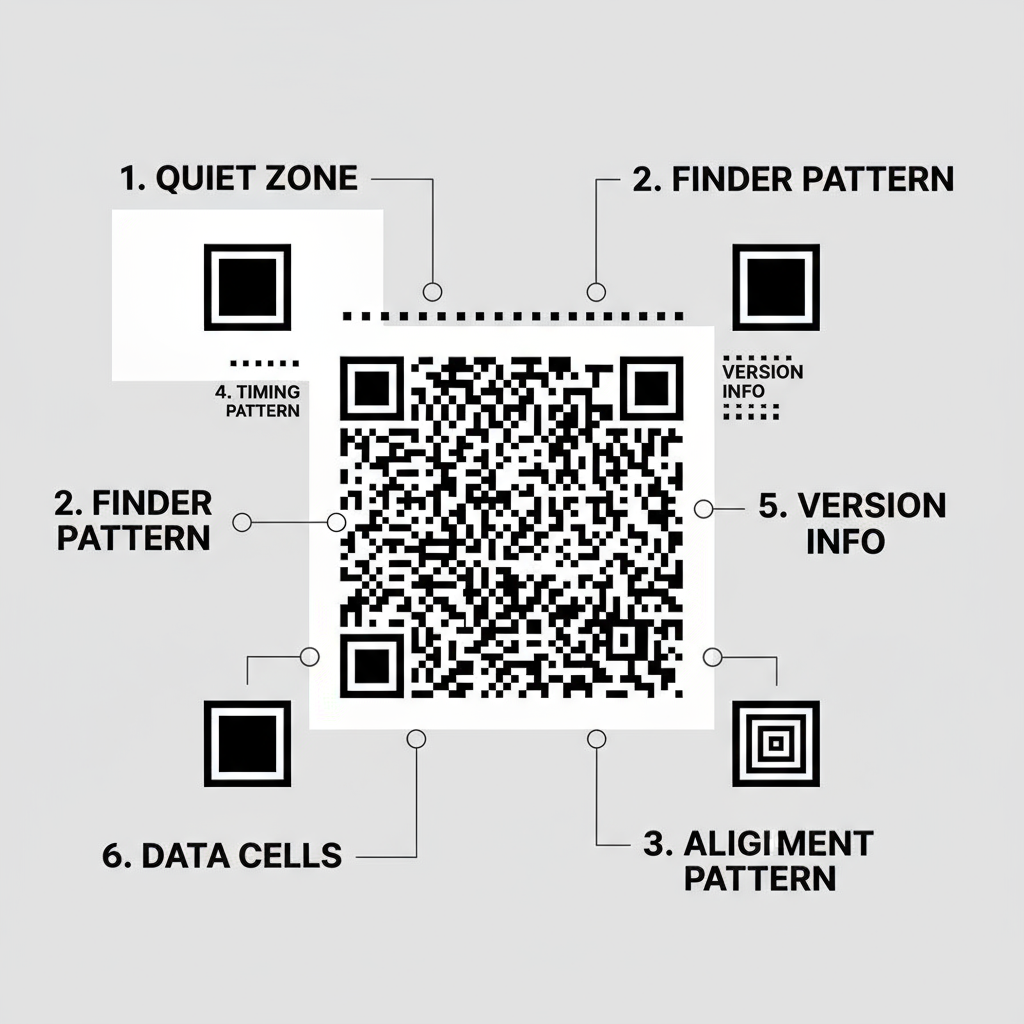
A typical QR code contains six important elements that make it readable and reliable:
1. Quiet Zone:
A blank border surrounding the QR code. Without it, the scanner wouldn’t know where the QR code begins or ends.
2. Finder Pattern:
The three large squares in the corners help scanners locate and identify the QR code, regardless of angle.
3. Alignment Pattern:
This small square near the bottom-right ensures the QR code can be scanned even if it’s distorted or tilted.
4. Timing Pattern:
An L-shaped line connecting finder patterns that help identify the size and structure of the QR code.
5. Version Information:
This defines the type or version of QR code, telling the reader how much data it holds.
6. Data Cells:
These small black and white boxes contain the actual data — URLs, text, or other information.
Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring that when you scan QR code, the information is accurate and readable.
Types and Modes of QR Codes
Input Modes of QR Codes
Depending on the type of data they store, QR codes operate in different modes:
- Numeric Mode: Stores only numbers (0–9). Can hold up to 7,089 digits.
- Alphanumeric Mode: Stores numbers, capital letters, and symbols like $, %, +, and –. Can hold up to 4,296 characters.
- Byte Mode: Stores binary data such as ASCII characters, with up to 2,953 characters.
- Kanji Mode: Used for Japanese characters, storing up to 1,817 characters.
There are also advanced modes like:
- Structured Append Mode: Splits large data across multiple QR codes.
- FNC1 Mode: Used in retail for barcode integration.
Common Styles of QR Codes
QR codes come in different shapes and forms:
- Standard QR Code: The original design with three black squares in corners.
- Aztec Code: Contains a single square in the center and is used in transport tickets.
- Maxicode: Used by postal services, featuring a circular pattern.
- PDF417: A rectangular barcode often used on ID cards or boarding passes.
- Semacode: A simplified version of the QR code used for web links.
Common Uses of QR Codes
QR codes are now part of daily life and business operations. Some of the most common uses include:
1. Marketing and Advertising
Marketers use QR codes on flyers, billboards, and packaging to direct users to websites, product pages, or offers instantly.
2. Digital Payments
From UPI payments in India to PayPal abroad, QR codes make transactions seamless and contactless.
3. COVID-19 Contact Tracing
During the pandemic, QR codes were used for safe check-ins and tracking virus exposure in public spaces.
4. Product Packaging
They reveal nutritional facts, warranty details, or promotional codes.
5. Education and Training
Institutes use QR codes for course materials, attendance, and library management.
6. Postal Services and Logistics
Companies like courier and retail brands use QR codes to track shipments and returns.
8. Are QR Codes Safe to Use?
This is where things get serious. While QR codes themselves are not dangerous, the links they contain can be. Cybercriminals exploit QR codes by embedding malicious URLs that lead to fake websites or initiate harmful downloads.
Common QR Code Security Threats:
- Phishing Sites: You scan a QR code and land on a fake website asking for your login details or banking info.
- Malicious Downloads: Some codes trigger automatic downloads of malware or spyware.
- Overlays on Genuine Codes: Attackers stick fake QR codes over legitimate ones (like payment boards at restaurants).
- Data Theft: Codes may redirect to sites that steal user data silently.
- Drive-By Attacks: Simply visiting a compromised website can trigger a virus or spyware download.
Since humans can’t read QR codes visually, users can’t verify if the destination is safe. This makes QR code security a growing concern in the digital age.
Can QR Codes Be Hacked?
Technically, the QR code itself cannot be hacked. However, the content or destination link can be maliciously designed to trick users.
For example, hackers may create a QR code that looks authentic but redirects you to a phishing page. Once you enter details like your username or card number, they capture it instantly.
Hence, the best practice is to only scan QR codes from trusted sources and verify the destination link before taking any action.
Do QR Codes Collect Personal Data?
This is another common question users ask — do QR codes collect my personal information?
The answer: QR codes themselves don’t collect personal data. However, the platforms or websites they link to might collect basic analytics, such as:
- How many times the QR code was scanned
- The location of scans
- Device type (Android/iPhone)
- Time and frequency of scans
This data helps businesses analyze engagement but does not include sensitive personal information unless users provide it themselves.
How to Stay Safe While Using QR Codes
To ensure QR code safety, here are some best practices to follow:
Before Scanning:
- Avoid scanning codes from unknown posters, messages, or emails.
- Check if the code has been tampered with (extra stickers or tape).
- Don’t scan codes on public notice boards or street poles.
While Scanning:
- Use a trusted QR scanner that previews links before opening them.
- If a link looks suspicious, don’t click on it.
- Disable automatic actions (like app downloads) in your QR reader settings.
After Scanning:
- Avoid entering personal or financial data on redirected websites.
- Keep your phone’s OS and antivirus up to date.
- Monitor your digital accounts for suspicious activity.
Tools for Safer QR Code Use
There are many QR scanner apps and built-in tools that offer additional layers of security. Look for scanners that:
- Provide URL previews before opening links.
- Detect suspicious or unsafe websites automatically.
- Keep a scan history log so you can track where you scanned codes.
Using a reliable QR scanner reduces the risk of phishing and malware infections.
Benefits of QR Codes (When Used Safely)

Despite potential risks, QR codes have several undeniable benefits:
- Convenience: Quick and contactless sharing of information.
- Speed: Instant access to digital platforms.
- Eco-friendly: Reduces paper usage in menus, tickets, and ads.
- Traceability: Ideal for logistics and inventory management.
- Marketing insights: Helps businesses understand customer engagement.
When used safely, QR codes are an excellent bridge between the physical and digital worlds.
The Future of QR Codes
The future of QR codes is bright and evolving. We can expect:
- Blockchain integration for authenticity and tamper-proof usage.
- Encrypted QR codes to prevent misuse.
- Augmented reality (AR) features where scanning brings interactive content.
- Expanded use in smart cities, healthcare, and education.
As technology advances, QR codes will continue to play a crucial role in digital communication and automation.
Conclusion
QR codes are among the most convenient and versatile tools in today’s digital landscape. From quick payments to instant access to data, they make life easier — but users must stay alert.
The QR code full form — Quick Response — reflects its speed and efficiency, but a quick response should not mean a careless one. Always verify sources before you scan QR code and use trusted QR scanners to protect yourself from scams and cyber threats.
With awareness and caution, QR codes can remain a safe and powerful tool for digital interaction.
FAQs
What is QR code full form?
QR stands for Quick Response. It was designed to quickly convey information when scanned by a digital device.
QR code kya hota hai?
QR code ek digital barcode hota hai jisme website link, text, ya payment information store hoti hai. Jab aap ise scan karte ho, phone aapko turant information dikha deta hai.
How do I scan QR code safely?
Always use a secure QR scanner that shows a link preview before opening it. Avoid scanning random codes from unknown sources.
Can scanning a QR code install a virus?
Not directly. But malicious QR codes can lead to infected websites that install malware or steal data.
Are QR code payments safe?
Yes, as long as you use official apps like Google Pay, PhonePe, or Paytm, and scan codes from verified merchants.
Do QR codes collect personal data?
No personal data is collected automatically. However, analytics such as scan time, location, and device type may be recorded.
How can I make QR code use more secure?
Use a trusted QR scanner, check for fake overlays, and never enter confidential details on unknown websites.
Debabrata Behera is a passionate blogger who writes about digital trends, personal growth, and practical insights, helping readers stay informed, inspired, and ready to achieve success in life.




