As cyber threats continue to evolve, malware is no longer just about causing visible damage or triggering obvious alerts. Modern threats are designed to hide, persist, and quietly compromise systems for extended periods. One such threat is the stealth virus. Unlike traditional malware that may slow down systems or display noticeable symptoms, a stealth virus is engineered to remain invisible while carrying out malicious activities in the background.
Understanding what is a stealth virus, how it operates, and how to protect against it is essential for anyone using computers in today’s digital environment. This guide provides a comprehensive explanation of stealth viruses, their behavior, risks, detection challenges, and prevention strategies.
What is a Stealth Virus?
A stealth virus is a type of malicious software that deliberately conceals its presence on an infected system. The defining characteristic of a stealth virus in computer systems is its ability to hide changes it makes to files, system processes, or memory. Its primary goal is to avoid detection by security tools while continuing to execute harmful tasks.
In simple terms, when people ask what is stealth virus, the answer is that it is malware designed to operate invisibly. It actively interferes with system monitoring tools so that infected files appear clean, unchanged, or normal even when they are not.
Stealth viruses often use advanced concealment techniques similar to those found in rootkits. Instead of simply infecting files, they manipulate system-level processes to hide their activities from the operating system itself.
How Stealth Viruses Work
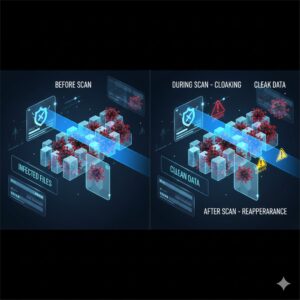
Stealth viruses work by masking their footprint within a system. When an operating system or security tool attempts to inspect an infected file, the stealth virus temporarily removes itself or presents a clean version of the file.
Common techniques used by stealth viruses include:
Intercepting system calls so file sizes appear unchanged
Replacing infected data with clean copies during scans
Manipulating memory to hide running malicious processes
Redirecting antivirus scans away from infected sectors
A stealth virus in computer environments does not rely on a single hiding method. Instead, it dynamically adapts its behavior based on system activity. If a scan is initiated, the virus hides. Once the scan is complete, it resumes its malicious operations.
This ability to actively respond to detection attempts is what makes stealth viruses particularly dangerous.
How Stealth Viruses Infect Computers
Stealth viruses infect systems using many of the same entry points as other malware, but with more advanced persistence mechanisms.
Common infection methods include:
Malicious email attachments that appear legitimate
Fake software installers masquerading as trusted programs
Unverified freeware or cracked software downloads
Compromised websites that silently deliver malicious code
Once executed, the stealth virus embeds itself deeply into the system. Unlike basic malware that may remain confined to a single file, stealth viruses often infect system files, boot sectors, or memory, making them extremely difficult to remove.
Stealth Virus Behavior Inside the System

After infection, a stealth virus begins monitoring system activity. It watches for signs that it might be detected, such as disk scans or file integrity checks.
Typical behaviors include:
Taking control of system interrupts
Modifying file system responses
Moving between drives or files to avoid deletion
Self-replicating into unused system areas
Stealth viruses may also degrade system performance subtly. Instead of obvious crashes, users may notice slight slowdowns, delayed application launches, or unexplained system behavior. These symptoms are often dismissed as normal performance issues, allowing the virus to remain active for long periods.
Why Stealth Viruses Are Hard to Detect
Stealth viruses are specifically designed to defeat traditional detection methods. Standard antivirus tools often rely on file signatures, behavior analysis, or integrity checks. A stealth virus interferes with all three.
Reasons detection is difficult include:
Infected files appear unchanged
Virus hides during scans
Malicious processes are masked in memory
System reports false clean results
Because stealth viruses can manipulate system responses, security tools may be scanning compromised data without realizing it. This creates a false sense of security, allowing the infection to persist undetected.
How to Detect a Stealth Virus
Detecting a stealth virus requires scanning the system from outside the infected environment. Running scans from within the compromised operating system may not reveal the infection.
Effective detection methods include:
Booting from an external clean disk
Running offline security scans
Comparing system files against trusted baselines
Monitoring unexplained system behavior
Even when detected, there is no guarantee the virus has not copied itself elsewhere. This is why stealth viruses are among the most difficult forms of malware to fully eliminate.
How to Remove a Stealth Virus
Removing stealth viruses is challenging and sometimes requires drastic measures. Because they can hide in multiple locations, deleting a single infected file is often insufficient.
Removal challenges include:
Hidden copies across drives
Reinfection after partial cleanup
Compromised system components
In severe cases, full system reinstallation may be the only reliable way to remove a stealth virus completely. Backups should be scanned carefully before restoration to avoid reinfection.
Also Read: What is Social Media Privacy and Prevention
How to Protect Yourself from Stealth Viruses
Prevention is far more effective than removal when dealing with stealth viruses. Strong cybersecurity habits significantly reduce risk.
Best practices include:
Avoid downloading software from untrusted sources
Do not open unknown email attachments
Keep operating systems updated
Use security tools capable of detecting hidden threats
Monitor unusual system behavior
Education and awareness play a critical role in preventing stealth virus infections.
Stealth Viruses vs Other Malware Types
Stealth viruses differ from other malware in several ways:
Traditional viruses cause visible damage
Trojans disguise themselves but do not hide once active
Worms spread rapidly but are detectable
Stealth viruses actively conceal their presence
This combination of persistence and invisibility makes stealth viruses more dangerous than many other malware types.
Real-World Risks of Stealth Viruses
The impact of a stealth virus in computer systems can be severe, even if symptoms appear minor.
Potential risks include:
Long-term data theft
Credential harvesting
Unauthorized surveillance
System integrity compromise
Undetected backdoors for future attacks
Because stealth viruses can remain hidden for extended periods, attackers may extract valuable data over time without alerting the victim.
Best Practices for Long-Term Protection
Long-term defense against stealth viruses requires layered security and vigilance.
Recommended strategies include:
Regular system audits
Secure boot practices
Controlled software installation policies
Employee and user awareness training
Continuous monitoring for anomalies
Strong digital hygiene is essential in defending against modern stealth-based threats.
Conclusion
Stealth viruses represent one of the most sophisticated and dangerous forms of malware in modern cybersecurity. Their ability to hide, adapt, and persist makes them especially difficult to detect and remove. Understanding what is a stealth virus, how it behaves, and how to defend against it is critical for maintaining system integrity.
While no system is completely immune, informed users and proactive security measures greatly reduce the risk. In a digital world where threats continue to evolve, vigilance remains the strongest defense.
FAQs
What is a stealth virus?
A stealth virus is malware that hides its presence by concealing changes made to files and system processes.
How does a stealth virus in computer systems remain undetected?
It intercepts system checks and presents clean data to security tools during scans.
Are stealth viruses still a threat today?
Yes, stealth viruses continue to evolve and remain a significant cybersecurity risk.
Can stealth viruses be completely removed?
Removal is difficult and may require offline scans or full system reinstallation.
How can users prevent stealth virus infections?
Avoid untrusted downloads, update systems regularly, and practice strong cybersecurity habits.




