In today’s hyper-connected digital world, data is constantly moving between devices, networks, servers, and cloud platforms. Whether you are sending an email, accessing a private company server, or browsing a website from a remote location, your information travels across multiple networks before reaching its destination. To make this communication possible and secure, systems rely on a structured set of rules known as protocols.
Among these, tunneling protocols play a critical role in enabling secure, private, and controlled data transmission across public and private networks. While often associated with secure connections and remote access, tunneling protocols are more complex than they appear and come with both benefits and risks.
This guide explains what a tunneling protocol is, how tunneling protocols work, where they are used, their security advantages, potential threats, and best practices for managing them safely.
What is Communication Protocols
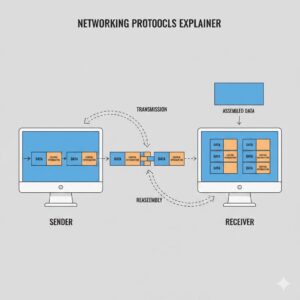
Before diving into tunneling protocols, it is important to understand what a protocol is in networking terms.
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that governs how data is transmitted, received, and interpreted between devices. When information is sent across a network, it is broken down into packets. Each packet contains two essential components:
- The actual data being transmitted
- Control information that defines how the data should be delivered, routed, and reassembled
Both the sending and receiving systems must follow the same protocol rules for communication to succeed.
What Is a Tunneling Protocol?
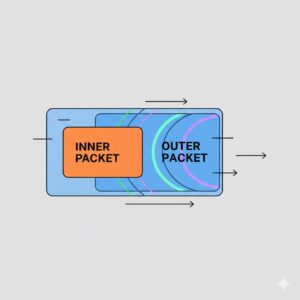
A tunneling protocol is a networking method that encapsulates one complete data packet inside another packet that uses a different protocol. In simple terms, it creates a virtual tunnel through which data can safely pass across a network that would otherwise not support or allow that type of traffic.
Instead of sending data directly, tunneling protocols wrap the original data packet inside an outer packet. This outer packet carries the tunneled data through the network until it reaches the destination, where it is unpacked and delivered in its original form.
This process allows data from a private network to travel securely over a public network without being directly exposed.
How Tunneling Protocols Work
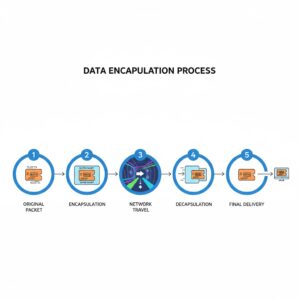
Tunneling protocols operate through a process known as encapsulation. Here is how it works step by step:
- A data packet is created using its original protocol
- That packet is wrapped inside another packet that follows a different protocol
- The outer packet travels across the network
- At the destination, the outer packet is removed
- The original packet is delivered to its intended endpoint
The tunnel itself acts as a protected pathway between two endpoints. Both endpoints must understand the tunneling protocol being used in order to establish and maintain the tunnel.
This method allows secure communication even when data is transmitted over networks that are not inherently secure.
Why Tunneling Protocols Are Used
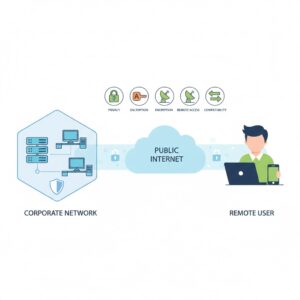
Tunneling protocols are primarily used to enable private communication over public infrastructure. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Transmitting private network data across the public internet
- Enabling remote access to internal systems
- Protecting unencrypted data during transmission
- Supporting virtual private network connections
- Allowing communication between incompatible network protocols
Without tunneling protocols, organizations would struggle to maintain privacy and data integrity across open networks.
Role of Tunneling Protocols in Virtual Private Networks
One of the most common applications of tunneling protocols is in virtual private networks.
A VPN relies on tunneling protocols to create a secure tunnel between a user’s device and a remote network. All data sent through this tunnel is encapsulated and protected, allowing users to access internal systems as if they were physically present on the network.
In this scenario, tunneling protocols ensure that:
- Data remains private while traveling across public networks
- Internal resources are protected from unauthorized access
- Communication appears seamless and continuous
Without tunneling protocols, secure remote connectivity would not be possible at scale.
Common Types of Tunneling Protocols
There are several tunneling protocols in use today, each designed for specific purposes and environments.
Secure Shell is commonly used for secure remote system access. It allows encrypted communication between two devices and is often used for administrative tasks.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol was designed to support early VPN connections. While simple to implement, it has largely been replaced by more secure alternatives.
Internet Protocol Security is widely used to secure internet communications by authenticating and encrypting data packets. It operates at the network layer and is often used in enterprise environments.
Each of these tunneling protocols serves a specific function and is selected based on security needs, compatibility, and performance requirements.
Security Benefits of Tunneling Protocols
Tunneling protocols offer several important security advantages.
They protect data confidentiality by hiding the original data packet within another packet. This makes it more difficult for attackers to inspect or alter the data during transmission.
They enable secure communication over untrusted networks by allowing sensitive information to travel safely across public infrastructure.
They help maintain data integrity by ensuring that information is not altered while in transit.
They support authentication mechanisms that verify the identity of devices and users at both ends of the tunnel.
Together, these benefits make tunneling protocols essential for modern secure networking.
Also Read: Is Incognito Mode Safe to Use? Pros and Cons of Using Incognito Mode
Risks and Misuse of Tunneling Protocols
Despite their benefits, tunneling protocols can also be misused.
Because tunneled traffic hides the original packet, attackers may use tunneling protocols to bypass poorly configured firewalls. By embedding restricted traffic inside allowed protocols, malicious data can pass through network defenses undetected.
Tunneling protocols can also reduce network visibility, making it harder for security tools to inspect traffic content.
In some cases, malware has been known to use tunneling techniques to communicate with command servers or transmit stolen data.
These risks highlight the importance of proper configuration and monitoring.
Challenges for Network Monitoring and Inspection
One of the biggest challenges introduced by tunneling protocols is reduced visibility.
Deep packet inspection tools analyze packet contents to detect suspicious activity. When packets are encapsulated, these tools may only see the outer packet, not the inner data.
Ingress and egress filtering systems that verify destination addresses may also struggle when traffic is tunneled.
As a result, tunneling protocols require more advanced monitoring strategies to ensure security without disrupting legitimate communication.
Tunneling Protocols and Malware Threats
In certain cases, attackers have used tunneling protocols to hide malicious activity.
By encapsulating malware traffic inside legitimate-looking packets, attackers can avoid detection and maintain persistent access to systems.
Newer technologies such as IPv6 tunneling have also been exploited in environments that are not fully compatible with newer protocols, creating additional security gaps.
This makes it essential for organizations to understand which tunneling protocols are active on their networks and how they are being used.
Who Needs to Worry About Tunneling Protocols
Tunneling protocols are mainly a concern for network administrators, IT teams, and cybersecurity professionals.
Organizations that manage enterprise networks must ensure that tunneling protocols are properly authorized, monitored, and secured.
While individual users benefit from tunneling protocols indirectly, system administrators are responsible for controlling how these tunnels are created and maintained.
Best Practices for Managing Tunneling Protocols
To safely use tunneling protocols, organizations should follow several best practices.
Unauthorized tunneling should be blocked through proper firewall configuration.
Known tunneling protocols should be explicitly allowed and monitored rather than left open by default.
Security policies should ensure that tunneled traffic is subject to the same inspection rules as standard traffic.
Network administrators should regularly review logs and traffic patterns to detect unusual tunneling behavior.
By applying these measures, organizations can balance security with functionality.
Why Tunneling Protocols Still Matter
Despite evolving security technologies, tunneling protocols remain essential.
Remote work, cloud computing, and distributed systems rely heavily on secure tunneling to function effectively.
When properly configured, tunneling protocols provide a reliable and secure method for transmitting data across complex network environments.
Understanding how they work and how to manage them responsibly is critical in modern networking.
FAQs
What is a tunneling protocol in simple terms?
A tunneling protocol is a method that wraps one data packet inside another so it can safely travel across a network that would not normally support that type of traffic.
Are tunneling protocols only used for VPNs?
No. While commonly used for VPNs, tunneling protocols are also used for secure remote access, protocol compatibility, and protecting unencrypted data.
Can tunneling protocols be dangerous?
They can be risky if misconfigured or abused, as they may hide malicious traffic from security tools.
Do tunneling protocols encrypt data?
Some tunneling protocols include encryption, while others rely on additional security mechanisms.
Who should manage tunneling protocols?
They should be managed by network administrators and IT professionals who understand network security and traffic control.
Conclusion
Tunneling protocols are a foundational component of modern networking. By encapsulating data inside secure pathways, they allow private communication across public and complex networks. From enabling remote access to supporting secure data exchange, tunneling protocols make today’s digital infrastructure possible.
However, their ability to hide data also introduces security challenges. Without proper oversight, tunneling protocols can be misused to bypass defenses or conceal malicious activity.
The key lies in understanding how tunneling protocols work, where they are used, and how to manage them responsibly. When implemented with strong security controls and continuous monitoring, tunneling protocols remain a powerful and necessary tool for secure communication in an interconnected world.




