Summary
In today’s digital world, every device connected to the internet has a unique identity — just like a home address in the physical world. This unique identity is known as an IP address. Whether you’re browsing social media, checking emails, or watching videos, your IP address is quietly working behind the scenes to connect your device to the web. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what an IP address is, how it works, its types, how to find it, and how you can protect it from hackers.
What is an IP Address?
Let’s start with the basics — what is an IP address?
An IP address (short for Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical label assigned to every device connected to a network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. Think of it as a digital identity for your computer, smartphone, or any other device that connects to the internet.
If you’ve ever wondered “IP address kya hota hai” or “IP address kya hai,” it simply means this: it’s a number that helps identify your device on a network, enabling data to reach the right destination.
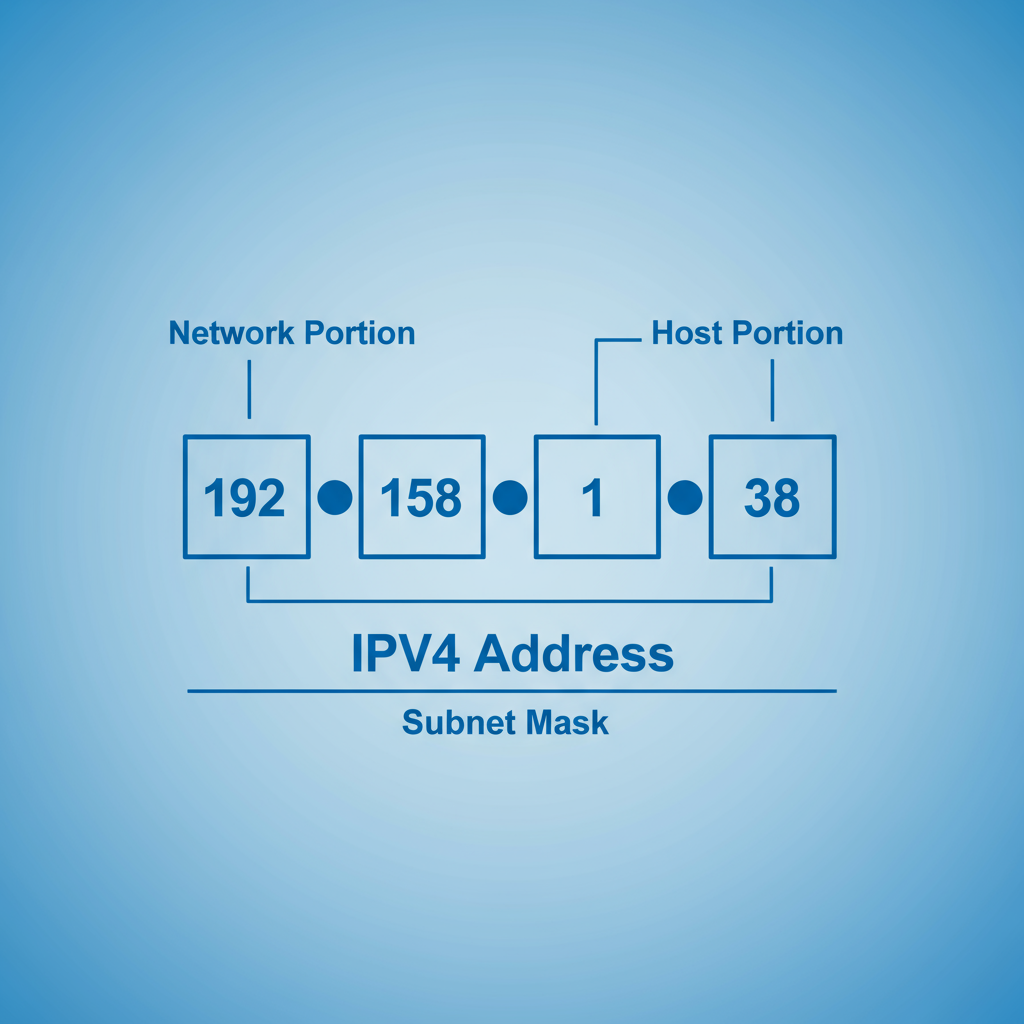
For example, an IP address looks like this:
192.158.1.38
It’s made up of four sets of numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by periods. This format is known as IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4). So, the possible range of IP addresses goes from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
Each IP address is unique and serves two main purposes:
- Identification: It identifies a specific device on a network.
- Location: It provides the location of that device within the network.
These addresses are not random; they are assigned systematically by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), which is part of the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) — a non-profit body managing internet resources globally.
How Do IP Addresses Work?
To understand what is IP address and how it functions, let’s imagine how communication works on the internet.
When you visit a website or send an email, your device sends a request to another computer (a web server) over the internet. The server responds to your request and sends the information back to your IP address.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how the process works:
- Your device connects to the internet through a network (usually your Internet Service Provider, or ISP).
- The ISP assigns an IP address to your device.
- When you access a website, your request goes through the ISP to the website’s server.
- The server identifies your device using the IP address and sends the response (webpage data) back to you.
- This exchange happens in milliseconds, allowing smooth communication online.
Interestingly, your IP address can change — for example, if you restart your modem, switch networks, or travel to another location. When you connect to a new Wi-Fi (like at a hotel or café), you’re temporarily assigned a new IP address by that network.
In short, IP addresses are like the internet’s language — they make sure every device can “talk” to another in a standardized and organized way.
Types of IP Addresses
There are different types of IP addresses based on how they’re used and assigned. Let’s explore them in detail.
A. Consumer IP Addresses
Every internet user has two types of IP addresses:
- Private IP Address
- Public IP Address
These two work together to ensure smooth communication between devices inside your network (like your Wi-Fi at home) and the outside world (the internet).
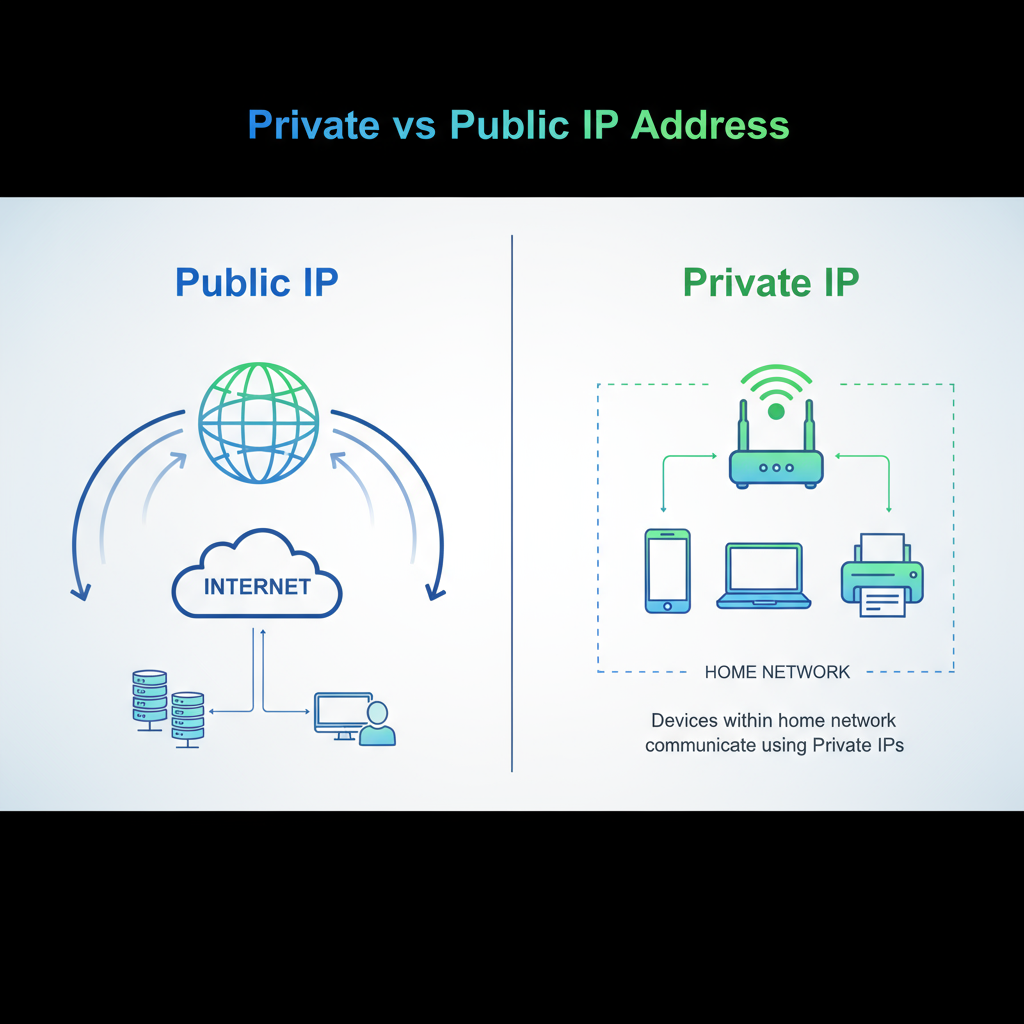
1. Private IP Address
A private IP address is used within your local network.
Every device connected to your Wi-Fi—smartphones, laptops, TVs, printers, or even smart home devices—has its own private IP address.
Your router assigns these private addresses automatically, ensuring that each device is identifiable within your home or office network.
For example:
- Your smartphone might have the private IP 192.168.0.2
- Your laptop might have 192.168.0.3
Even though these devices share the same internet connection, their private IPs help the router know which device is which.
2. Public IP Address
A public IP address is your network’s unique identity on the internet.
While your router assigns private IPs to devices inside your network, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) assigns a public IP to your router.
This public IP is visible to websites and other servers you connect with online. When you search “What is my IP” on Google, the number that appears is your public IP address.
B. Types of Public IP Addresses
There are two main types of public IP addresses:
1. Dynamic IP Address
A dynamic IP address changes periodically.
Your ISP assigns a new IP from a large pool whenever you connect to the internet. This process helps ISPs manage addresses efficiently and enhances user security.
Benefits of dynamic IPs:
- Lower cost for ISPs
- Enhanced security (harder to hack)
- Automatically refreshed over time
2. Static IP Address
A static IP address does not change. Once assigned, it remains constant.
Static IPs are commonly used by businesses that host websites, email servers, or databases. Having a fixed IP ensures reliable connectivity and easy accessibility.
Website IP Addresses
For website owners, there are two more categories of IPs to understand:
1. Shared IP Address
Most small websites use shared hosting plans.
In this setup, multiple websites are hosted on the same server, meaning they all share one IP address. This is economical and works fine for low-traffic websites.
2. Dedicated IP Address
A dedicated IP is assigned exclusively to one website.
It allows easier setup of SSL certificates, enables FTP access, and lets you access your site directly using the IP instead of a domain name. This is ideal for larger or more secure websites.
How to Find Your IP Address
There are two kinds of IPs you can check — public and private.
To find your public IP:
- Simply type “What is my IP address” in Google.
- Websites like WhatIsMyIP or IPLocation will display it instantly.
To find your private IP:
On Windows:
- Press Windows + R, type cmd, and hit Enter.
- In Command Prompt, type ipconfig and press Enter.
- Look for “IPv4 Address” – that’s your private IP.
On Mac:
- Open System Preferences → Network.
- Select your network and view details.
On iPhone:
- Go to Settings → Wi-Fi.
- Tap the “i” icon next to your connected network.
- Your IP will be shown under the DHCP section.
IP Address Security Threats
Now that you understand what is IP address, it’s time to talk about its risks.
Just like your home address, your IP can expose information about your location and network. Cybercriminals can misuse it in many ways.
1. Social Engineering Attacks
Hackers may trick you into revealing your IP via messaging apps or fake links. Once they know it, they can attempt to trace your location or launch attacks.
2. Online Stalking
Your IP can sometimes be visible when playing online games or commenting on forums. Attackers can use tracking tools to find your approximate location.
3. Illegal Downloads
If hackers get hold of your IP, they might use it to download pirated or illegal content — which can falsely link you to cybercrimes.
4. DDoS Attacks
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack floods your network with traffic, causing your internet connection to crash. This is common in gaming communities and online businesses.
5. Direct Device Hacking
Each IP has thousands of “ports.” Hackers can exploit these to try and gain unauthorized access to your device, install malware, or steal sensitive data.
How to Protect and Hide Your IP Address
Protecting your IP address is crucial for maintaining online privacy and security. Here are the best ways to do it:
A. Use a Proxy Server
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet.
Instead of connecting directly, your traffic is routed through the proxy. The websites you visit only see the proxy’s IP, not yours.
However, not all proxies are safe — some may monitor your data or inject ads.
B. Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN is a much safer and more effective method.
When you connect to a VPN, your data is encrypted and sent through a secure tunnel to a VPN server, hiding your real IP address.
This means no one — not even your ISP — can see what you’re doing online.
Benefits of using a VPN:
- Protects against hackers on public Wi-Fi
- Allows access to blocked or restricted websites
- Prevents tracking and surveillance
- Keeps browsing anonymous
When Should You Use a VPN?
1. While Using Public Wi-Fi
Public networks (like in cafes or airports) are often unsecure. A VPN encrypts your connection, keeping your data safe from prying eyes.
2. While Traveling
Some countries restrict websites like YouTube or Facebook. A VPN lets you access them by routing your traffic through another region.
3. For Remote Work
If you’re working from home, a VPN ensures a secure connection to your company’s network, protecting sensitive data.
4. For Privacy at Home
Even at home, websites and advertisers can track your IP to target you with personalized ads. Using a VPN helps you stay private.
Other Ways to Protect Your Privacy
1. Adjust Privacy Settings
Ensure that messaging and calling apps only allow connections from your contacts. This minimizes IP exposure.
2. Use Strong Passwords
Always create unique, complex passwords with a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols.
3. Avoid Phishing Links
Be cautious when opening suspicious emails or clicking on unknown links — they can expose your IP or install malware.
4. Install and Update Antivirus Software
Antivirus programs can block malware, detect suspicious network activity, and protect your device from unauthorized access.
Conclusion
To sum up, an IP address is the backbone of how the internet functions. It connects your device to the world, enabling seamless communication and data transfer. However, just like any digital identifier, it also needs protection.
Understanding what is IP address, how it works, and how to safeguard it is vital for your online security.
By using tools like VPNs, strong passwords, and updated antivirus software, you can protect your digital footprint and browse safely.
So, the next time someone asks “IP address kya hota hai” or “IP address kya hai,” you’ll know exactly how to explain it — it’s your digital home address on the internet!
FAQs
What is an IP address in simple words?
An IP address is a unique number that identifies your device on the internet or a local network, allowing it to send and receive information.
IP address kya hota hai?
IP address ek unique number hota hai jo aapke device ko internet ya network par pehchanta hai. Isse hi data aapke system tak pahuchta hai.
What are the two main types of IP addresses?
The two main types are private IP (used inside a network) and public IP (used on the internet).
How can I find my IP address?
You can type “What is my IP” on Google or check your network settings on your device to find it.
Can someone hack me using my IP address?
If hackers know your IP, they can attempt to track your location or launch attacks. Using a VPN can prevent this.
What’s the difference between static and dynamic IP addresses?
Static IPs stay the same, while dynamic IPs change automatically from time to time.
How can I protect my IP address?
Use a VPN, avoid sharing personal links with strangers, and install good antivirus software.
Debabrata Behera is a passionate blogger who writes about digital trends, personal growth, and practical insights, helping readers stay informed, inspired, and ready to achieve success in life.




