Web browsers have become the primary gateway to the internet. From checking emails and managing finances to collaborating on cloud-based tools, almost everything we do online happens through a browser. Unfortunately, this also makes browsers one of the most attractive targets for cybercriminals. Malicious websites, infected ads, phishing pages, and hidden scripts are all designed to exploit browser vulnerabilities and gain access to devices or networks.
As cyber threats grow more advanced and harder to detect, traditional security tools are often not enough on their own. This is where browser isolation comes in. Browser isolation is a modern security approach that focuses on containing threats rather than trying to block every malicious file or website. Instead of trusting the web, it assumes the internet is hostile by default and isolates browsing activity from the user’s device.
In this article, we will explore what is browser isolation, how it works, why it is gaining popularity, the difference between browser isolation and remote browser isolation, and how it helps protect individuals and organizations from web-based threats.
What Is Browser Isolation?

Browser isolation is a cybersecurity technique that separates web browsing activity from the user’s actual device or internal network. Instead of loading websites directly on a local browser where malicious code can interact with the operating system, browser isolation runs all web content in a secure, isolated environment such as a virtual machine or sandbox.
This isolated environment acts as a protective barrier. Any malicious code, scripts, or downloads encountered while browsing remain trapped inside the isolation layer and never reach the user’s device. As a result, even if a user visits a compromised or malicious website, their system stays protected.
Browser isolation is also commonly referred to as web isolation. While it has traditionally been used by large organizations and IT departments, it is increasingly being recognized as a valuable security layer for remote workers, small businesses, and security-conscious individuals.
At its core, browser isolation follows a zero-trust philosophy. It assumes that every website could be dangerous and treats all web content as untrusted unless proven otherwise.
Why Web Browsers Are a Major Security Risk

Modern websites are built using a combination of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. While HTML and CSS mainly define structure and appearance, JavaScript is a full programming language capable of executing complex actions. This makes it powerful, but also risky.
Most browsers automatically execute JavaScript code when a webpage loads. Cybercriminals exploit this behavior by embedding malicious scripts into websites, ads, or compromised platforms. A single visit to the wrong page can trigger malware downloads, credential theft, or silent tracking.
Common browser-based threats include phishing pages designed to steal login credentials, malicious advertisements that redirect users to infected sites, and drive-by downloads that exploit browser vulnerabilities. Because these threats often look legitimate, users may not realize they are under attack until damage is done.
Browser isolation addresses this risk by removing the browser as a direct attack surface.
How Browser Isolation Works
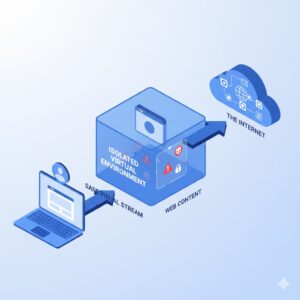
To understand how browser isolation works, it helps to first look at how traditional browsing works. Normally, when you visit a website, the browser downloads and executes all associated code directly on your device. If that code is malicious, it can interact with your operating system, files, or network.
Browser isolation changes this model completely.
When browser isolation is enabled, web content is not executed on the user’s device. Instead, it is processed in an isolated environment that is separate from the endpoint. This environment may exist locally on the device or remotely on a secure server.
The user interacts with a safe representation of the webpage rather than the webpage itself. In many implementations, the user receives a visual stream of the content, such as pixels or rendered output, while the actual code runs elsewhere.
If malware is encountered, it remains confined within the isolated session. When the browsing session ends, the entire environment is destroyed and reset. This ensures that no malicious files, scripts, or changes persist.
From the user’s perspective, browsing feels normal. Pages load, links work, and web applications function as expected. Behind the scenes, however, the browser is fully separated from the device, dramatically reducing risk.
The Zero-Trust Approach in Browser Isolation
A key principle behind browser isolation is zero trust. Rather than trying to decide which websites are safe and which are not, browser isolation assumes that all web content is potentially dangerous.
This approach is important because attackers are constantly finding new ways to bypass filters and detection-based security tools. A website that appears legitimate today could be compromised tomorrow. Even secure-looking websites with HTTPS encryption can host malicious scripts.
By isolating all browsing activity, browser isolation eliminates the need to trust web content. Instead of relying on blacklists or signatures, it focuses on containment. If a threat appears, it is neutralized automatically by isolation.
Types of Browser Isolation
Browser isolation can be implemented in different ways depending on where the isolated environment is hosted and how it interacts with the user.
Remote browser isolation is the most common and widely discussed implementation. In this model, all browsing activity is executed on a remote server, usually in the cloud. The user’s device never directly processes the web code. Instead, it receives a safe stream of the rendered webpage. This approach provides strong security because threats are kept far away from the endpoint.
On-premise browser isolation works in a similar way but uses servers managed internally by an organization. This is often chosen by companies with strict compliance or data residency requirements. While it offers greater control, it also requires more infrastructure and maintenance.
Client-side browser isolation runs the browser locally but inside a sandbox or virtualized environment on the device. While this approach still improves security, it relies on the endpoint’s resources and may offer slightly less protection than remote isolation.
Regardless of the method used, all types of browser isolation share a common goal: preventing web-based threats from reaching the user’s system.
Difference Between Browser Isolation and Remote Browser Isolation
The terms browser isolation and remote browser isolation are often used interchangeably, but there is an important distinction.
Browser isolation is a broad concept that refers to isolating web browsing activity from the endpoint. It includes all approaches, whether isolation happens locally, on-premise, or remotely.
Remote browser isolation is a specific type of browser isolation where the isolated environment is hosted on a remote server, usually in the cloud. The browser session runs entirely off the user’s device, and only safe visual output is delivered to the endpoint.
The main difference between browser isolation and remote browser isolation lies in where the isolation occurs. Remote browser isolation generally provides stronger security because it removes web execution completely from the endpoint. It also reduces the risk of local vulnerabilities being exploited.
However, remote browser isolation may require more bandwidth and careful performance optimization. Client-side isolation, while slightly less secure, can be easier to deploy in certain scenarios.
Understanding this difference helps organizations choose the right model based on their security needs, resources, and user experience requirements.
Also Read: What Is Blockchain Security?
Threats Browser Isolation Defends Against
Browser isolation is effective against a wide range of web-based attacks. One of the most dangerous is the drive-by download, where simply visiting a webpage triggers the download of malicious software without user interaction.
Malvertising is another major threat. In these attacks, malicious code is injected into legitimate advertising networks. Users may be infected even when visiting trusted websites because the ads themselves carry the payload.
Click-jacking attacks trick users into clicking on hidden or disguised elements, leading to unintended actions such as granting permissions or downloading malware.
Browser isolation also protects against redirect attacks, where users are silently redirected from legitimate websites to attacker-controlled pages. Cross-site scripting attacks, which inject malicious scripts into trusted websites, are also neutralized because scripts run in isolation.
Even advanced attacks that exploit browser vulnerabilities are rendered harmless, since the compromised environment is destroyed after the session ends.
Why Browser Isolation Is Becoming More Popular
Several trends are driving the growing adoption of browser isolation. One of the biggest is the increase in sophisticated cyber attacks. Phishing campaigns, ransomware, and zero-day exploits are becoming more targeted and harder to detect.
Another major factor is the rise of remote and hybrid work. Employees often access corporate resources from home networks or personal devices that may not be as secure as office environments. This increases the risk of web-based attacks entering corporate systems.
Traditional security tools often focus on detecting known threats. However, attackers frequently use new techniques that evade detection. Browser isolation shifts the focus from detection to containment, making it effective even against unknown threats.
Organizations are also looking for ways to reduce alert fatigue. By isolating web threats automatically, browser isolation reduces the number of security incidents that require investigation.
Benefits of Browser Isolation
One of the biggest advantages of browser isolation is protection from malicious websites. Since web content never touches the endpoint, users are shielded from hidden threats.
Browser isolation also provides strong protection against malicious emails. Web-based email platforms are rendered safely, and links are opened within the isolated environment, preventing phishing and malware delivery.
Malicious downloads are either blocked or sanitized before reaching the user. Administrators can define policies that control which file types are allowed.
Another important benefit is data loss prevention. Browser isolation can restrict copy-paste actions, file uploads, or downloads, reducing the risk of sensitive data being leaked intentionally or accidentally.
From an organizational perspective, browser isolation can provide insights into user behavior without exposing systems to risk. It also lowers the cost associated with cleaning infected devices and recovering from malware incidents.
Browser Isolation for Organizations and Individuals
While browser isolation has traditionally been associated with enterprises, its value extends beyond large organizations. Remote workers, freelancers, and individuals who frequently browse unfamiliar websites can all benefit from this technology.
For businesses, browser isolation supports secure access to cloud applications, third-party platforms, and research websites without exposing internal networks. It complements existing security tools rather than replacing them.
For individuals, browser isolation provides peace of mind when browsing the web, opening links, or accessing unfamiliar content.
FAQs
What is browser isolation in simple terms?
Browser isolation is a security method that keeps web browsing separate from your device so that malicious websites cannot harm your system.
How does browser isolation improve security?
It prevents web-based threats from interacting with your operating system by running browsing activity in an isolated environment.
What is the difference between browser isolation and remote browser isolation?
Browser isolation is a general concept, while remote browser isolation specifically runs browsing sessions on remote servers instead of the user’s device.
Does browser isolation affect browsing performance?
Most modern solutions are optimized to provide a smooth browsing experience, though performance depends on implementation and network quality.
Is browser isolation suitable for small businesses?
Yes, browser isolation is increasingly used by small businesses and remote teams to protect against web-based threats.
Conclusion
As the internet continues to evolve, so do the threats that come with it. Web browsers remain one of the most common entry points for cyber attacks, making them a critical focus for modern security strategies.
Browser isolation offers a powerful and forward-looking solution by separating browsing activity from the user’s device. Instead of trying to identify every possible threat, it assumes the web is untrusted and contains risks by default.
By understanding what is browser isolation, how it works, and the difference between browser isolation and remote browser isolation, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions about protecting their digital environments. In a world where browsing safely is more important than ever, browser isolation stands out as a strong and reliable line of defense.




