In today’s highly interactive digital environment, users click buttons, links, pop-ups, and banners almost instinctively. While this behavior enables smooth navigation and convenience, it also opens the door to a subtle yet dangerous cyber threat known as clickjacking. Many users interact with malicious content without realizing it, believing they are clicking something harmless when in reality they are authorizing actions they never intended.
Clickjacking attacks continue to be a serious concern because they exploit human trust and normal browsing behavior rather than technical weaknesses alone. Understanding clickjacking meaning, how a clickjacking attack works, and how to protect yourself is essential for anyone who uses the internet regularly.
This guide provides a complete explanation of clickjacking, its risks, real-world examples, and proven prevention strategies.
Clickjacking Meaning and Definition
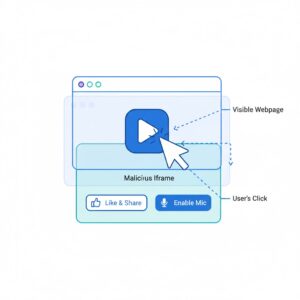
Clickjacking is a cyberattack technique that tricks users into clicking on something different from what they perceive on their screen. In simple terms, clickjacking hides malicious actions behind legitimate-looking buttons, links, or user interface elements.
When users interact with a webpage, they believe they are clicking a visible button or link. However, attackers place a hidden layer over the page, often invisible or transparent, that captures the click and redirects it to perform a malicious action instead. This deceptive technique is also known as user interface redressing or UI redress attacks.
The danger of click jacking lies in the fact that users do not need to download anything or knowingly interact with suspicious content. A single click can authorize actions such as granting permissions, transferring money, enabling a webcam, or submitting credentials.
What Is Clickjacking and Why It Is Dangerous
To understand what is clickjacking, it is important to recognize that the attack does not target software vulnerabilities directly. Instead, it targets users. The website may appear legitimate and function normally, making the attack extremely difficult to detect.
Clickjacking attacks are dangerous because they can lead to serious consequences, including unauthorized financial transactions, account compromise, identity theft, privacy violations, and malware installation. Since the interaction looks normal from the user’s perspective, victims often remain unaware that an attack has occurred.
Unlike traditional malware attacks that rely on downloads or suspicious files, clickjacking can happen instantly and silently through everyday browsing.
How Does a Clickjacking Attack Work
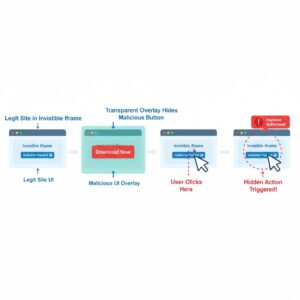
Clickjacking works primarily through the use of HTML frames and iframes. An iframe allows one webpage to be embedded inside another. While this technology is commonly used for legitimate purposes, such as embedding videos or external content, attackers exploit it for malicious intent.
In a clickjacking attack, the attacker loads a legitimate webpage within an invisible iframe. On top of this iframe, they place a transparent or disguised layer containing malicious code or actions. The user sees only the visible page and interacts with it normally.
When the user clicks a button, link, or form field, the click is actually captured by the hidden iframe rather than the visible element. This allows the attacker to execute actions without the user’s knowledge.
Clickjacking does not rely solely on mouse clicks. It can also manipulate text input, dragging actions, and touch interactions, making it effective across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices.
Social engineering often plays a role in luring users to malicious pages. Attackers may use emails, advertisements, social media posts, or fake news headlines to attract clicks.
What Can Clickjacking Attacks Do
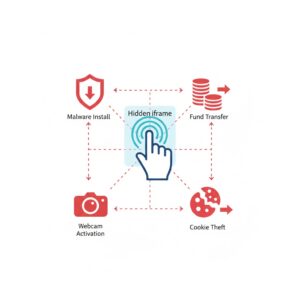
A successful clickjacking attack can trigger a wide range of malicious actions. These actions depend on what the attacker has hidden behind the visible interface.
Common outcomes of clickjacking attacks include installing malicious software on a device, stealing login credentials by capturing form inputs, activating webcams or microphones without consent, authorizing unwanted money transfers, making online purchases, revealing a user’s location, or manipulating social media interactions such as likes, shares, and subscriptions.
In some cases, clickjacking is used to inflate advertising metrics or generate fraudulent engagement, which can harm advertisers, platforms, and users alike.
Because the attack operates silently, victims may not notice any immediate signs of compromise.
Types of Clickjacking Attacks
Clickjacking attacks come in several variations, each designed to exploit different aspects of user interaction.
Likejacking is a form of clickjacking that targets social media platforms. Users believe they are clicking a harmless button, but in reality, they are liking, sharing, or following content they did not intend to support.
Cursorjacking manipulates the position of the cursor so that it appears in one location while the actual click registers elsewhere. This misalignment causes users to interact with hidden malicious elements.
Cookiejacking is used to steal browser cookies. These cookies often contain session data that attackers can use to impersonate users and gain access to accounts without passwords.
Filejacking exploits file upload interfaces. When users click a button to upload a file, attackers can gain unauthorized access to parts of the local file system, potentially exposing sensitive data.
Each type of clickjacking attack leverages deception rather than brute force, making them particularly effective.
Real-World Clickjacking Examples
Clickjacking is not a theoretical threat. Real-world incidents have demonstrated its potential impact.
In some cases, attackers have exploited payment platforms by embedding malicious frames that authorize transactions with a single click. Users who were already logged in unknowingly transferred funds to attacker-controlled accounts.
Mobile malware campaigns have also used clickjacking techniques to gain elevated permissions. Once installed, the malware overlaid invisible screens that captured user interactions, allowing attackers to read messages, access contacts, and intercept verification codes.
These examples highlight how clickjacking attacks can scale rapidly and affect users across multiple countries and platforms.
Risks and Impact of Clickjacking
The risks associated with clickjacking extend beyond individual users. Businesses and organizations can suffer financial losses, data breaches, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
For individuals, the impact may include identity theft, unauthorized transactions, privacy violations, and compromised accounts. For businesses, clickjacking can lead to loss of customer trust, fraudulent activity, and operational disruption.
Because clickjacking attacks often go unnoticed, damage may continue until it is discovered through unusual account behavior or financial discrepancies.
Clickjacking Prevention for Individuals
While no defense is perfect, users can significantly reduce their risk by adopting safe browsing habits.
Be cautious of emails or messages that create urgency and push you to click links immediately. Avoid downloading apps or software from unknown or unofficial sources. Treat advertisements that seem too good to be true with skepticism, especially on search engines and social media platforms.
Typing website addresses directly into the browser instead of clicking links can reduce exposure to malicious pages. Awareness remains one of the most effective defenses against clickjacking.
Browser-Level Protection Against Clickjacking
Modern browsers include built-in mechanisms to warn users about suspicious websites. However, additional browser extensions can provide extra protection.
JavaScript-blocking tools and anti-clickjacking extensions can prevent hidden scripts from executing. While these tools may require configuration and may disrupt some website functionality, they offer an added layer of security for users who want stronger control.
Maintaining an allowlist of trusted websites can help balance security and usability.
System-Level and Software Protection
Keeping operating systems, browsers, and applications updated is critical. Updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
Using comprehensive security software helps detect malicious scripts, block suspicious websites, and monitor unusual activity in real time. Layered security provides stronger protection than relying on a single defense.
Best Cyber Hygiene Practices
Good cyber hygiene reduces exposure to clickjacking and many other threats. Avoid using pirated software or unofficial services, as these are common sources of malicious scripts.
Review permissions granted to websites and apps regularly. Limit access to sensitive features such as cameras, microphones, and location services unless necessary.
Staying informed about evolving attack techniques helps users adapt their defenses and remain vigilant.
Conclusion
Clickjacking is a deceptive yet powerful cyber threat that exploits user trust rather than technical flaws alone. By hiding malicious actions behind familiar interfaces, attackers can cause significant harm with minimal effort.
Understanding clickjacking meaning, recognizing how a clickjacking attack works, and implementing practical prevention strategies are essential steps toward safer online behavior. While technology provides some protection, informed and cautious users remain the strongest defense.
By combining awareness, browser protections, secure software practices, and mindful interaction with online content, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risks posed by clickjacking attacks.
FAQs
What is clickjacking in simple terms
Clickjacking is a technique where users are tricked into clicking something different from what they see, causing unintended and often harmful actions.
How dangerous is a clickjacking attack
A clickjacking attack can lead to financial loss, identity theft, privacy breaches, and malware infections, making it a serious security threat.
Can clickjacking steal personal data
Yes, clickjacking can capture login credentials, session cookies, and other sensitive information.
How can users detect clickjacking
Clickjacking is difficult to detect visually, but unusual account activity or unexpected actions after clicking may indicate an attack.
Are modern browsers safe from clickjacking
Modern browsers offer some protection, but users should still follow safe browsing practices and consider additional security tools for better defense.




