In today’s hyper-connected digital world, malicious threats evolve faster than ever. Whether you browse the internet, use mobile banking, download apps, or shop online, you’re continuously exposed to cyber risks. One of the biggest dangers lurking across the digital landscape is malware. But what is malware exactly? Why is it considered one of the most damaging cybersecurity threats? And how does it impact individuals and organizations worldwide?
This comprehensive guide will help you understand the true meaning of malware, how it spreads, its most common types, warning signs of infection, and essential tips on protection and removal. The more informed you are, the better equipped you will be to defend your digital life from malicious attacks.
What Is Malware? Understanding the Threat

Malware is short for malicious software, a broad category of harmful programs intentionally developed to infiltrate, damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to a device, network, or system.
Cybercriminals design malware for various purposes, including:
- Stealing personal, financial, and confidential information
- Encrypting or corrupting data and demanding payment for recovery
- Taking control of devices to launch large-scale attacks
- Monitoring user activities and collecting sensitive behavior data
- Destroying system functions or networks
This means malware isn’t just irritating computer glitches. It can lead to:
- Identity theft
- Financial losses
- Data breaches
- Privacy invasion
- Business shutdowns and operational disruptions
Both individuals and organizations can become victims, and consequences can escalate quickly if threats go undetected.
Malware is constantly evolving as attackers create new methods to bypass security systems. Being aware of how malware works is the first step toward staying secure.
How Does Malware Spread?
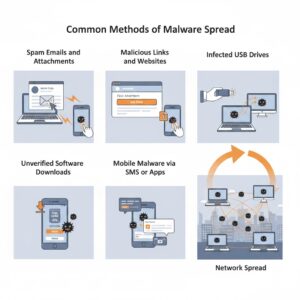
Malware infections typically occur when users unknowingly interact with malicious content. Attackers take advantage of curiosity, convenience, and trust. Some of the most common methods include:
Spam Emails and Attachments
Phishing emails often disguise themselves as trusted contacts or legitimate companies. Opening an attachment or clicking a link can instantly install malware.
Malicious Links and Websites
Fake advertisements, fraudulent pages, and compromised websites can trigger automatic downloads, injecting malware into your system.
Infected USB Drives and Removable Media
A single compromised USB device can spread malware to every system it connects with, making it a favored technique in corporate espionage.
Software Downloads from Unverified Sources
Free software, cracked programs, or apps from unofficial stores often contain embedded malware.
Mobile Malware via SMS or Apps
Fake applications, misleading text messages, and unsafe app permissions can easily compromise smartphones.
Regardless of the method, once malware infiltrates a device, it can spread across networks like wildfire, infecting multiple connected systems.
Types of Malware: A Deep Dive Into Major Threats
Malware isn’t one specific threat; it includes many different forms that operate in unique ways. Understanding the major categories helps users recognize risks and take proper defensive actions.
Worms
Worms are self-replicating malware programs that spread automatically without user action. They exploit vulnerabilities in networks or operating systems. Worms can:
- Consume system resources
- Disrupt network performance
- Deliver harmful payloads such as ransomware
Because they multiply rapidly, worms can cause large-scale damage within organizations.
Also Read: What Is Steganography? Definition and Explanation
Adware
Adware generates unwanted advertisements on devices. It collects browsing behavior and displays intrusive pop-ups and redirects. While some adware is merely annoying, others may:
- Track private browsing habits
- Download additional malware secretly
- Open backdoors for hackers
Unsuspecting users might install adware bundled with free apps.
Spyware
Spyware secretly monitors a user’s activities and transmits sensitive information to attackers. It can:
- Log keystrokes to capture passwords and banking details
- Read emails and chat messages
- Track browsing history and behavior patterns
Spyware stays hidden to maintain silent surveillance for as long as possible.
Viruses
Much like biological viruses, computer viruses attach themselves to legitimate files or programs and spread through user interaction. Viruses can:
- Modify system files
- Delete data
- Corrupt software and slow system performance
Opening the wrong attachment or file is often enough to trigger infection.
Bots
Bots are automated malware programs. When millions of infected devices are linked together, they form a botnet controlled by cybercriminals. Botnets are used to:
- Launch Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks
- Spread spam and other malware
- Steal sensitive data
Device owners often don’t realize their system is being used as a cyberweapon.
Ransomware
Ransomware is one of the most devastating types of malware. It encrypts data and demands payment for access restoration. Victims often face:
- Permanent data loss
- Business downtime
- Financial extortion with no guarantee of recovery
Hospitals, government institutions, and major companies have suffered catastrophic ransomware attacks.
Trojans
Trojans disguise themselves as trustworthy files, tricking users into installing them. Once inside, they can:
- Steal banking credentials
- Spy on users
- Download additional malware
- Provide remote access to attackers
Types include:
- Downloaders
- Banking Trojans
- Backdoor Trojans
- Spy Trojans
Their deceptive nature makes them especially dangerous.
Fileless Malware
Fileless malware does not rely on stored files. Instead, it hides in system memory and uses legitimate tools, making detection extremely difficult. It leaves almost no traces behind, allowing attackers to persist undetected.
How to Detect Malware Infection
Cybercriminals design malware to stay hidden as long as possible. However, changes in device behavior often signal something is wrong. Common symptoms include:
- Sluggish performance and slow startup
- Frequent crashes and unresponsive apps
- Unexpected pop-ups even when not browsing
- Increased data consumption without explanation
- Browsers redirecting to unfamiliar pages
- New, unknown apps appearing suddenly
- Rapid battery drain and overheating
- Security warnings urging immediate purchase of tools
- Locked or encrypted files
If multiple signs appear at once, infection is highly likely and should be addressed immediately.
How to Remove Malware Safely
Once malware is detected, quick action minimizes long-term damage. Recommended steps include:
- Install and update trusted security software
- Perform a full system scan and quarantine malicious files
- Disconnect the device from the internet during removal
- Reboot in Safe Mode if malware persists
- Clear temporary files using built-in utilities
- Update all operating systems, apps, and browsers
- Reset affected passwords and enable stronger authentication
- Rescan the system to confirm threat elimination
In extreme cases, a complete system restore or reinstall might be necessary.
Best Practices for Malware Protection
Defense is always more effective than cure. Implementing strong cybersecurity habits reduces risks of infection significantly. Here are the most important protection practices:
- Use reputable antivirus and security tools
- Enable real-time protection on all devices
- Keep software and operating systems updated
- Download apps only from official stores like Google Play and the Apple App Store
- Evaluate developer credibility and user reviews before installation
- Avoid apps with few downloads or suspicious ratings
- Carefully review requested permissions
- Never click unknown attachments or email links
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication
- Avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive tasks or connect through a secure VPN
Cyberthreats evolve, but security practices evolve too. Maintaining vigilance is essential for safety.
Why Protecting Against Malware Matters
As businesses continue expanding their online presence and individuals rely more heavily on digital connections, malware becomes an even greater threat. The consequences of a successful attack can include:
- Identity theft and stolen money
- Fraudulent purchases or unauthorized transfers
- Loss of valuable files and sensitive data
- Harm to reputation or business operations
Recovery often takes time, effort, and cost. Preventive action is always better than reacting after damage is done.
FAQs
What does malware stand for?
Malware stands for malicious software designed to harm systems, steal data, or disrupt operations.
Can malware affect smartphones and tablets?
Yes. Mobile malware is increasing rapidly and can infect devices through unsafe apps, malicious links, or unsecured Wi-Fi.
Is every slow device infected with malware?
Not always. Slow performance could have many causes, but sudden major changes may indicate infection.
Should ransomware victims pay the ransom?
Security experts strongly advise against paying ransom because attackers may not unlock files after receiving money.
How often should users update their devices?
Updates should be installed as soon as they are available, since they patch discovered vulnerabilities.
Can malware steal passwords?
Yes. Spyware and keyloggers specifically target login credentials and personal information.
Conclusion
Malware remains one of the biggest threats in the digital world. It comes in many forms and can strike any device at any moment. Understanding what malware is, how it spreads, and how to detect and remove it empowers you to take control of your cybersecurity posture.
With the right protection strategies and awareness, you can defend your devices, secure your personal data, and navigate the online world with greater confidence.




