The world of cryptocurrency has transformed the way people view money, transactions, and digital ownership. At the heart of this revolution lies an essential process known as crypto mining. But what is crypto mining, and why does it matter?
Crypto mining, short for cryptocurrency mining, is the process that validates transactions and adds them to a blockchain network. It is the backbone that keeps cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum running securely and reliably. By solving complex mathematical problems, miners confirm transactions, create new blocks, and are rewarded with newly minted coins and transaction fees.
In this guide, we’ll explore the definition of crypto mining, how it works, the advantages and disadvantages of mining, the differences between legitimate mining and cryptojacking, and how to protect yourself from crypto-related threats.
Crypto Mining: Meaning and Core Concept
Crypto mining is the process of verifying and recording cryptocurrency transactions on a blockchain — a decentralized, public digital ledger. Every time a user sends or receives cryptocurrency, that transaction must be validated to prevent fraud, double-spending, or manipulation.
Unlike traditional financial systems where a central authority, such as a bank, confirms transactions, blockchain networks rely on a distributed network of users called miners. These miners use high-powered computers to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. Once a puzzle is solved, a new block of verified transactions is added to the blockchain.
In return, the miner receives a reward in the form of newly created cryptocurrency tokens and transaction fees. This reward system incentivizes miners to continue validating transactions, thereby maintaining the network’s security and functionality.
Essentially, crypto mining serves two critical functions:
- It ensures that cryptocurrency transactions are secure and legitimate.
- It releases new coins into circulation, similar to how central banks issue fiat currency.
How Crypto Mining Works
To understand how crypto mining works, it’s important to grasp the basics of blockchain technology and the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism.
Blockchain Basics
A blockchain is a digital ledger composed of linked blocks of data. Each block contains:
- Transaction details
- A timestamp
- A cryptographic hash of the previous block
This structure makes the blockchain secure and immutable. Any attempt to alter one block would require changing all subsequent blocks, which is computationally infeasible.
Proof of Work and Mining
Most cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, use a system called Proof of Work. Under PoW, miners compete to solve mathematical problems that require significant computational power. The first miner to find the correct solution earns the right to add a new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with cryptocurrency.
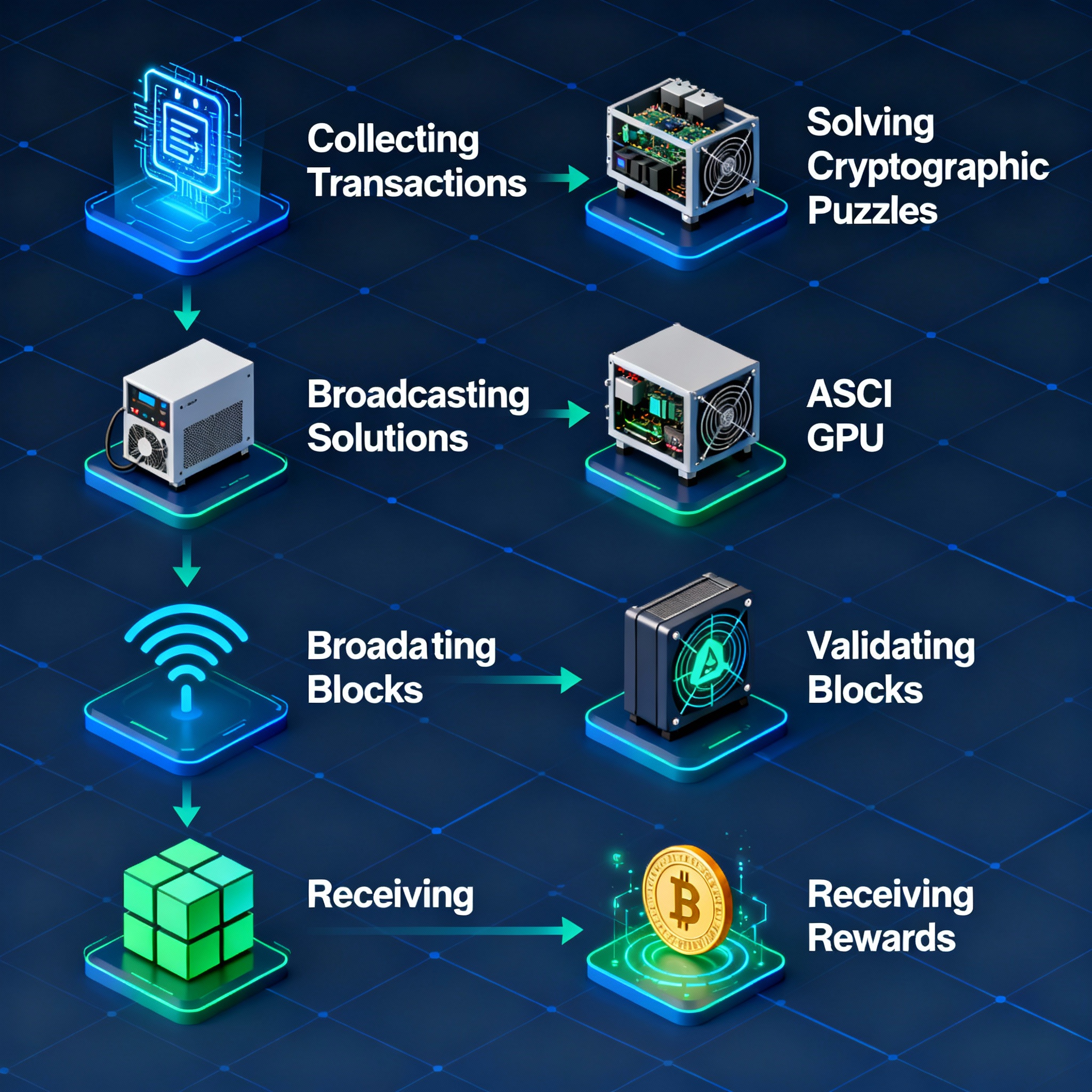
Mining Process
- Transaction Collection: Miners collect pending transactions from the network.
- Puzzle Solving: Miners use specialized hardware to solve a cryptographic puzzle.
- Block Validation: Once a miner finds a valid solution, it is broadcasted to the network for verification.
- Block Addition: If verified, the block is added to the blockchain.
- Reward Distribution: The miner receives a reward — both newly minted coins and transaction fees.
Difficulty Adjustment
As more miners join the network, the system automatically adjusts the difficulty level to maintain a consistent rate of block creation. For instance, Bitcoin adjusts its mining difficulty approximately every two weeks to ensure that blocks are produced roughly every ten minutes.
Reward Halving
To control supply and mimic scarcity, some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin undergo halving events. During halving, the mining reward is cut in half every few years, making new coin generation slower and reinforcing scarcity.
This process ensures that crypto mining remains competitive, secure, and economically balanced.
What Miners Need: Equipment and Tools
Mining cryptocurrency is not as simple as using an ordinary computer. It requires specialized equipment, software, and a stable power supply.
Mining Hardware
- ASIC Miners (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits):
These are purpose-built machines optimized for mining specific cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. ASICs are extremely efficient but expensive and often become outdated as technology advances. - GPU Miners (Graphics Processing Units):
GPUs, commonly used for gaming or rendering graphics, are ideal for mining certain cryptocurrencies like Ethereum (before its switch to Proof of Stake). They are more flexible than ASICs but consume more power.
Mining Software
Mining software allows miners to control hardware, connect to mining pools, and monitor performance. It facilitates communication between the mining hardware and the blockchain network.
Wallet
A crypto wallet is essential for storing the mined coins. It can be either a hot wallet (connected to the internet) or a cold wallet (offline for better security). Wallets also generate private keys, which are crucial for accessing and transferring funds.
Mining Pools
A mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computational resources to increase the chances of solving puzzles and earning rewards. The rewards are then distributed proportionally based on each miner’s contribution.
Power Supply and Cooling
Mining consumes enormous amounts of energy. Therefore, miners need a reliable power supply and an efficient cooling system to prevent hardware from overheating. Many large-scale mining operations are located in regions with cheap electricity and cooler climates.
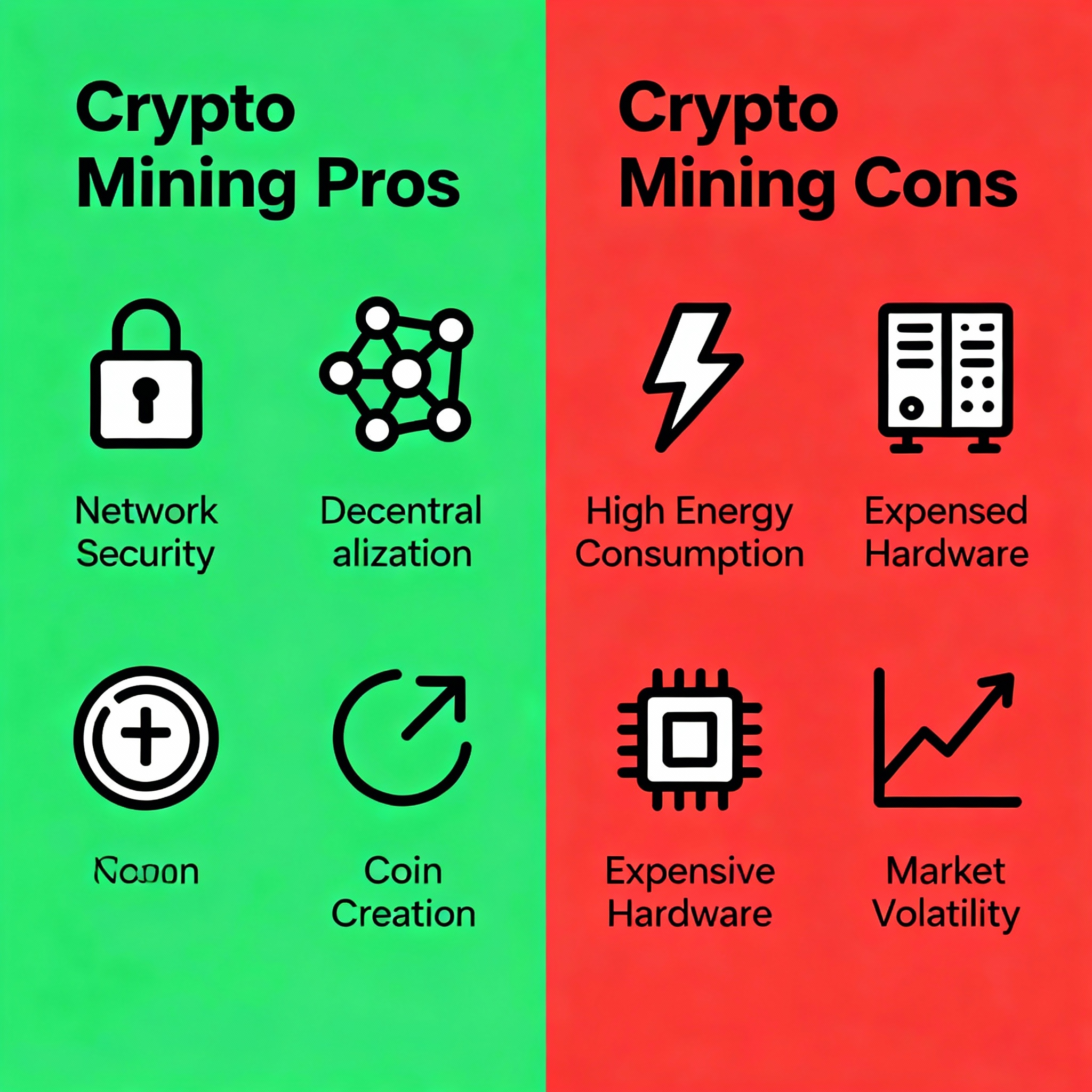
Advantages of Crypto Mining
Despite its complexity, crypto mining offers several benefits to both miners and the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Network Security
Mining plays a crucial role in securing blockchain networks. The Proof of Work system makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to manipulate transaction data, as it would require immense computational power to alter the blockchain.
Creation of New Coins
Mining introduces new coins into circulation, maintaining a steady supply of cryptocurrency and ensuring that the ecosystem continues to function.
Decentralization
Crypto mining contributes to decentralization, one of the core principles of blockchain technology. Instead of relying on a central authority, miners worldwide collectively maintain the network.
Support for Smart Contracts and Applications
In addition to transactions, mining also powers decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts, which automate digital agreements without intermediaries.
Innovation and Competition
Mining drives technological innovation. The constant pursuit of efficiency has led to advancements in hardware, energy management, and computational techniques.
Downsides of Crypto Mining
While crypto mining has numerous benefits, it also comes with significant challenges.
High Energy Consumption
Crypto mining requires substantial electrical power, particularly for Proof of Work cryptocurrencies. This heavy consumption raises concerns about the environmental impact of mining operations, especially those relying on non-renewable energy sources.
Hardware Costs and Maintenance
Mining equipment like ASICs and GPUs is expensive to purchase and maintain. The hardware also becomes obsolete quickly as mining difficulty increases and technology evolves.
Centralization Risks
Although mining is meant to be decentralized, large mining pools often dominate the network. This concentration of power can potentially threaten blockchain security, leading to risks such as a 51% attack, where one group gains majority control.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Cryptocurrency regulations vary by country and are still evolving. Some nations have banned mining altogether, citing environmental concerns and financial risks. This uncertainty can make mining risky for businesses and individuals.
Market Volatility
Mining profitability depends heavily on cryptocurrency prices. When prices drop, operational costs can exceed rewards, making mining unprofitable.
Environmental Impact
The high electricity consumption associated with mining contributes to carbon emissions, especially in areas where energy sources are fossil-fuel-based. As environmental awareness grows, mining sustainability has become a hot topic globally.
Cryptojacking vs Mining Malware
As crypto mining gained popularity, cybercriminals found ways to exploit it for illegal profit through cryptojacking and mining malware.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is the unauthorized use of someone else’s computing power to mine cryptocurrency. Hackers often install malicious scripts or software on devices, allowing them to secretly mine coins while the victim’s system slows down and consumes more power.
Mining Malware
Mining malware refers to programs designed to infiltrate computers and mine cryptocurrency without user consent. This type of malware operates stealthily, often spreading through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or unpatched software vulnerabilities.
While both cryptojacking and mining malware involve unauthorized mining, cryptojacking typically runs scripts through web browsers, whereas mining malware embeds itself within the system.
Signs of Crypto Mining Malware
If your computer or mobile device has been infected with crypto mining malware, you may notice the following signs:
- Reduced performance: Your system becomes unusually slow, as CPU and GPU resources are redirected toward mining tasks.
- Overheating: Continuous mining activity generates excessive heat, which can lead to hardware damage or thermal throttling.
- High electricity bills: Unexplained spikes in energy usage may indicate background mining processes.
- Unusual network activity: Mining malware communicates with remote servers to transmit mined coins.
- New or unknown processes: Unknown programs running in the background may signal a malware infection.
- Browser slowdowns: Some websites use embedded mining scripts that utilize your computer’s power without permission.
How to Protect Against Crypto Mining Threats
Protecting yourself from unauthorized crypto mining requires vigilance and strong cybersecurity habits. Here are some essential steps:
- Use reliable antivirus or anti-malware software to detect and block mining malware.
- Keep your operating system, browsers, and software updated to close security loopholes.
- Avoid suspicious links, pop-ups, or email attachments that could install malware.
- Enable your firewall to block unwanted network connections.
- Install ad blockers and browser extensions that prevent mining scripts from running.
- Regularly monitor your CPU, GPU, and network usage for unusual activity.
- Educate yourself about safe online practices and be cautious when downloading files.
- Secure your Wi-Fi network with strong passwords to prevent external access.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for all crypto and email accounts to enhance security.
Following these measures can help protect your devices, data, and privacy from cryptojacking and mining malware.
FAQs
What is crypto mining and how does it work?
Crypto mining is the process of verifying and adding transactions to a blockchain network using computational power. Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles, and the first to succeed adds a new block to the blockchain and earns cryptocurrency rewards.
What are the dangers of crypto mining malware?
Mining malware secretly uses your device’s resources to mine cryptocurrency, leading to reduced performance, overheating, higher electricity bills, and potential data breaches.
How does cryptojacking differ from legitimate mining?
Legitimate mining occurs with the owner’s consent, using personal or rented hardware. Cryptojacking, on the other hand, exploits someone else’s device without permission to perform mining tasks.
Is crypto mining legal?
In most countries, crypto mining is legal, but regulations vary. Some governments have banned or restricted mining due to energy and environmental concerns.
Can I mine cryptocurrency on my laptop?
While technically possible, mining on a regular laptop is inefficient and can cause overheating or hardware damage. Dedicated mining rigs are far more effective.
Is crypto mining profitable?
Mining profitability depends on several factors — cryptocurrency price, hardware efficiency, electricity costs, and mining difficulty.
What is a 51% attack?
A 51% attack occurs when a single miner or group controls over half of the blockchain’s computational power, enabling them to manipulate transactions.
Conclusion
Crypto mining is a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. It validates transactions, secures networks, and distributes new coins — all without the need for a central authority. However, it’s not without challenges. High energy costs, expensive equipment, market volatility, and environmental concerns continue to shape the future of mining.
As the industry evolves, new technologies such as Proof of Stake (PoS) aim to provide more energy-efficient alternatives. Yet, understanding how crypto mining works remains essential for anyone exploring the world of digital currencies.
By staying informed, practicing good cybersecurity hygiene, and recognizing the risks, users can engage safely with this transformative technology while contributing to the future of decentralized finance.




