As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity, organizations face increasing pressure to protect their networks, data, and users from a wide range of digital risks. Malware, phishing, ransomware, spyware, and network intrusions no longer operate in isolation. Instead, modern attacks often combine multiple techniques at once, making traditional single-purpose security tools less effective.
This growing threat landscape has given rise to a more consolidated approach to cybersecurity known as Unified Threat Management, commonly referred to as UTM. A unified threat management system brings multiple security functions together into one centralized solution, simplifying network protection while improving visibility and control.
In this guide, we will explore the UTM meaning, understand the unified threat management definition, examine how UTM works in cybersecurity, and discuss its advantages, limitations, and real-world use cases.
What Is Unified Threat Management (UTM)?
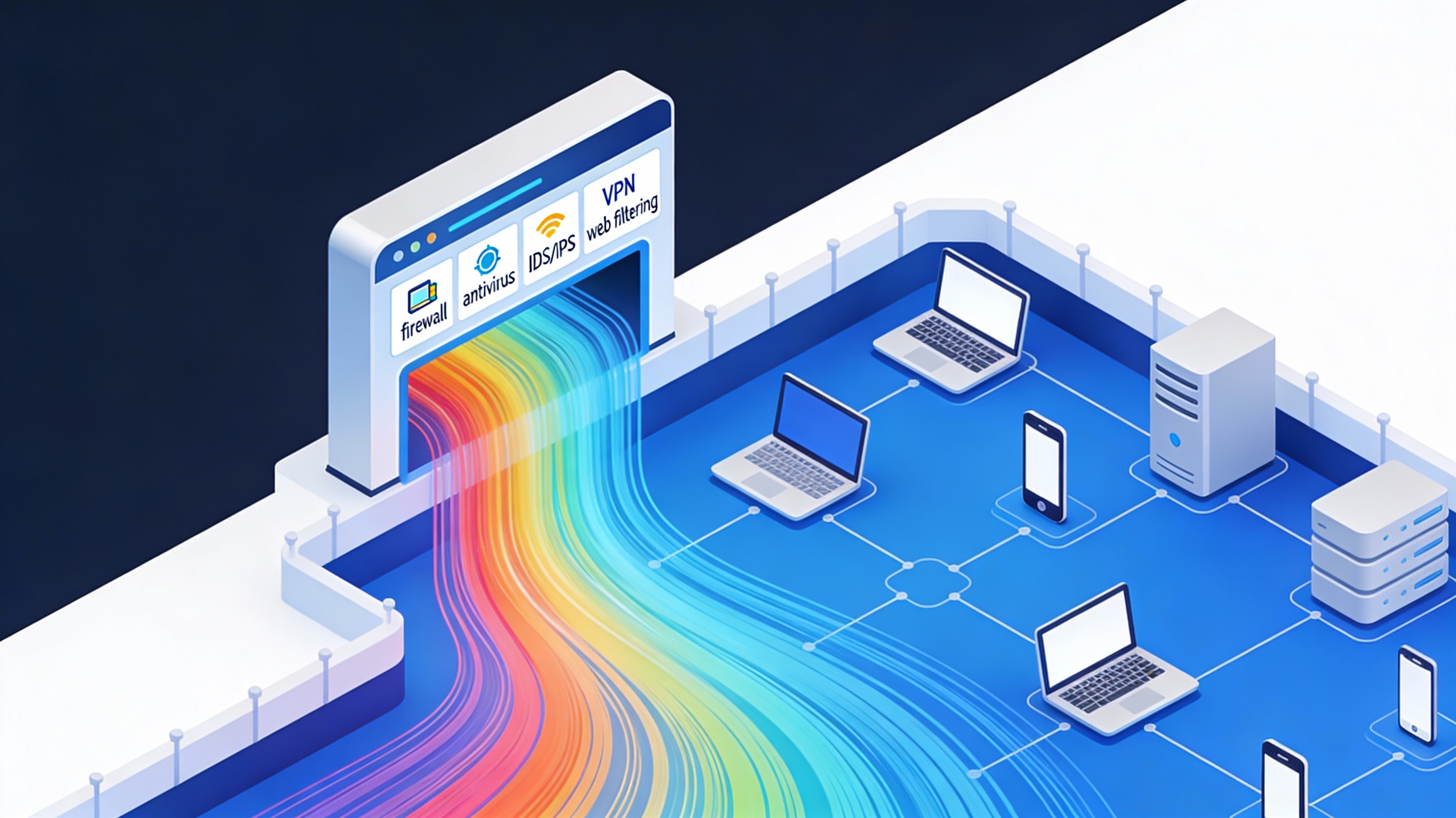

Unified Threat Management Definition
Unified Threat Management is a cybersecurity approach that integrates multiple security services into a single platform or appliance. Instead of managing separate tools for firewall protection, antivirus scanning, intrusion detection, content filtering, and spam control, UTM consolidates these capabilities into one system.
In simple terms, the UTM meaning in cybersecurity refers to an all-in-one security solution designed to protect a network from a wide range of threats through a centralized interface.
A unified threat management system typically sits at the network perimeter and acts as the first line of defense, monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic while enforcing security policies across the organization.
Why Unified Threat Management Is Important Today
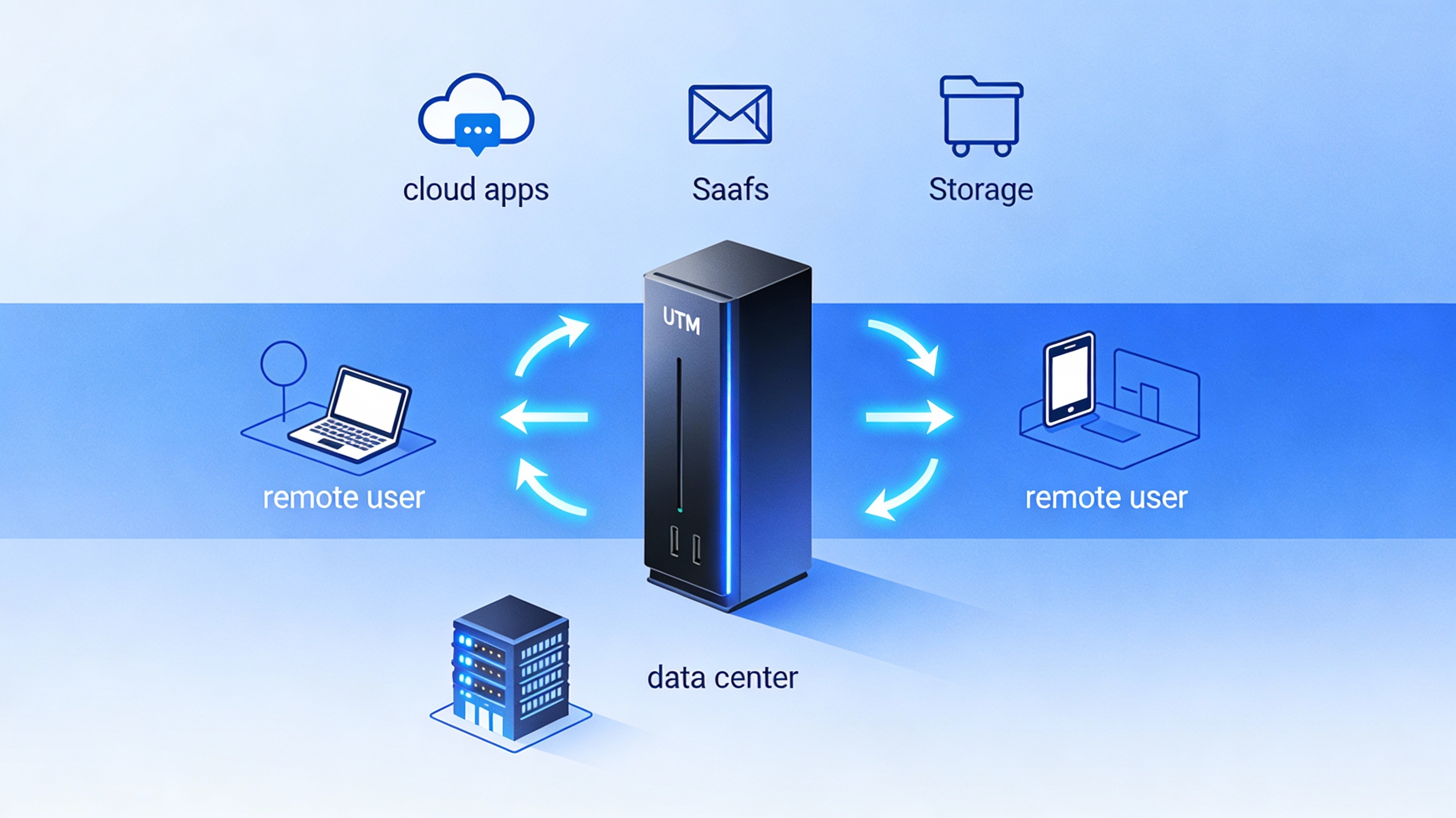
The modern digital environment is highly interconnected. Employees work remotely, applications run in the cloud, and sensitive data flows constantly between systems. This interconnectedness increases the attack surface and makes it harder to manage security using isolated tools.
Unified threat management addresses this challenge by:
- Reducing complexity in cybersecurity operations
- Improving visibility into network threats
- Providing consistent security policies across systems
- Lowering the burden on IT teams
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated and frequent, organizations increasingly rely on unified security platforms to stay ahead of threats without overwhelming their resources.
Core Components of a Unified Threat Management System
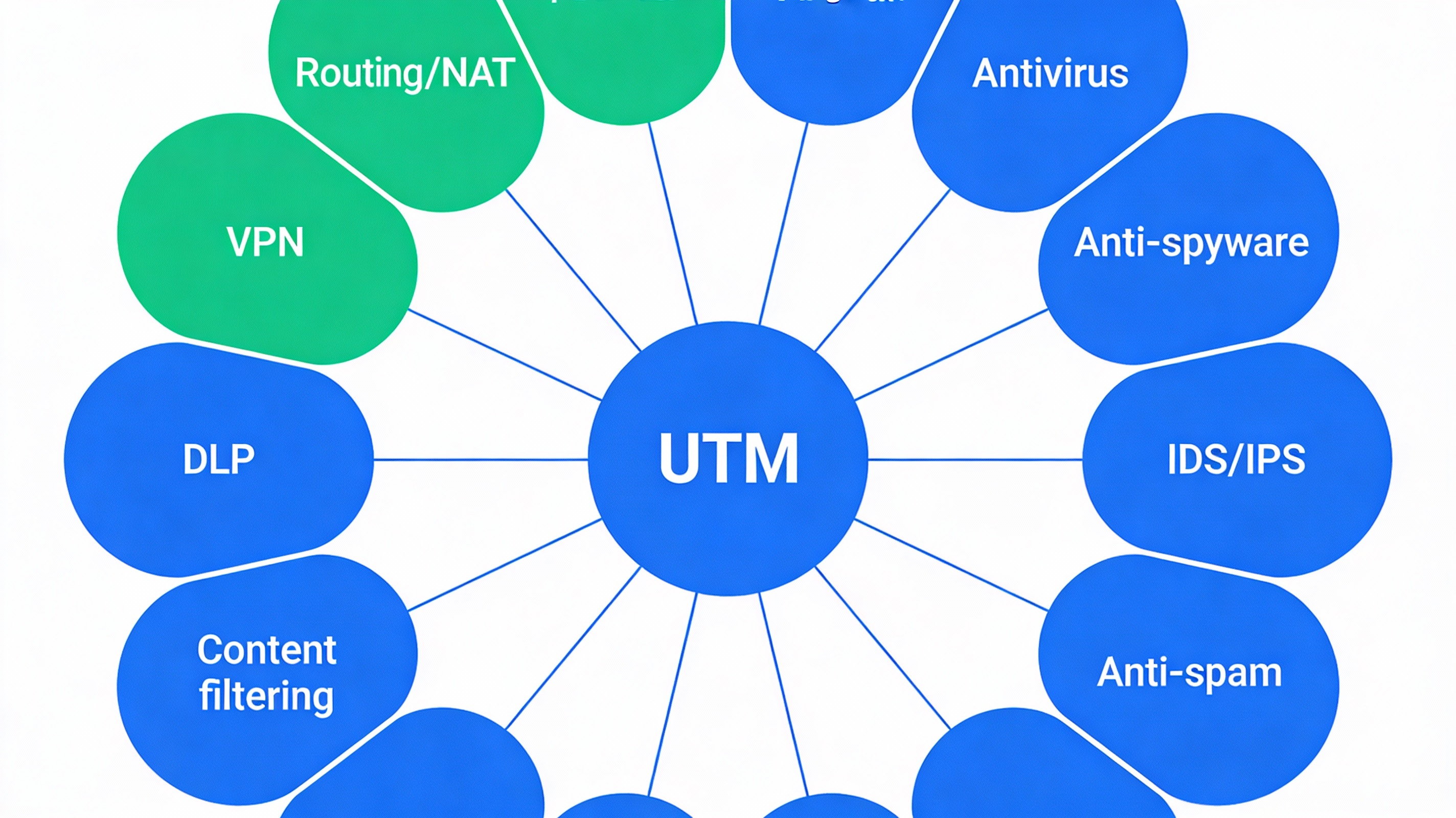
A unified threat management system combines several essential security functions into one integrated solution. While features may vary between vendors, most UTM platforms include the following components.
Firewall Protection
The firewall is the foundation of any UTM system. It controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules, blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication.
Antivirus and Anti-Malware
UTM systems scan files, downloads, and network traffic for known malware signatures and suspicious behavior. This helps prevent viruses, worms, trojans, and other malicious software from entering the network.
Anti-Spyware Protection
Spyware can secretly collect user data and monitor activity. Unified threat management solutions detect and block spyware before it compromises sensitive information.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Intrusion detection identifies suspicious activity within the network, while intrusion prevention actively blocks attacks in real time. Together, these systems protect against exploits, brute-force attacks, and unauthorized access attempts.
Also Read: What is a Stealth Virus?
Anti-Spam Filtering
Spam emails are a common entry point for phishing attacks and malware. UTM platforms filter unwanted messages before they reach users, reducing exposure to email-based threats.
Content Filtering
Content filtering allows organizations to control access to websites and online content. This helps prevent users from visiting malicious or inappropriate sites and improves productivity.
Data Leak Prevention
Some unified threat management systems include tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving the network unintentionally or maliciously.
Virtual Private Network Support
VPN capabilities allow secure remote access to the network by encrypting data transmitted over public connections. This is essential for remote work and branch office connectivity.
Network Address Translation and Routing
UTM devices often provide routing and address translation features, enabling secure and efficient traffic management within the network.
How Unified Threat Management Protects Against Modern Cyber Threats
Understanding Blended Threats
Blended threats combine multiple attack methods into a single campaign. For example, a phishing email may deliver malware that opens a backdoor, allowing attackers to launch further intrusions or steal data.
Traditional security tools struggle to stop blended threats because each tool operates independently. Unified threat management systems overcome this limitation by coordinating multiple security functions within one platform.
Centralized Threat Detection
By analyzing traffic at a single point, UTM systems can correlate data across different security layers. This allows faster identification of suspicious behavior and more effective threat mitigation.
Real-Time Protection
Unified threat management solutions continuously monitor network activity and apply security updates to respond to emerging threats as they appear.
Advantages of Unified Threat Management
Simplified Security Management
One of the biggest advantages of UTM is simplicity. Instead of managing multiple vendors and interfaces, administrators can control all security functions from a single console.
Cost Efficiency
Using a unified threat management system can be more affordable than purchasing and maintaining separate security appliances, especially for small and medium-sized organizations.
Improved Visibility
Centralized monitoring provides a comprehensive view of network activity, making it easier to identify vulnerabilities and respond to incidents.
Consistent Security Policies
UTM ensures that security rules are applied uniformly across the network, reducing gaps that attackers could exploit.
Reduced Administrative Overhead
With fewer systems to configure and update, IT teams can focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance.
Limitations and Risks of Unified Threat Management
While unified threat management offers many benefits, it is not without challenges.
Single Point of Failure
Because UTM consolidates multiple security functions into one system, a failure can impact all defenses simultaneously. This is why some organizations add additional security layers as backups.
Performance Constraints
High traffic volumes can strain UTM appliances, potentially affecting network performance if the system is not properly sized.
Scalability Concerns
Large enterprises with complex networks may find that a single unified threat management system does not scale as easily as specialized, distributed security solutions.
Vendor Dependency
Relying on one provider for multiple security functions can limit flexibility and customization.
Best Practices for Using Unified Threat Management Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness of a unified threat management system, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Regularly update security signatures and firmware
- Monitor logs and alerts proactively
- Combine UTM with endpoint and cloud security tools
- Conduct periodic risk assessments
- Implement network segmentation to limit the impact of breaches
Unified threat management works best as part of a layered security strategy rather than as a standalone solution.
UTM vs Traditional Multi-Vendor Security Solutions
Traditional security architectures rely on multiple specialized tools, each handling a specific function. While this approach can offer flexibility, it also increases complexity.
Unified threat management systems simplify security by integrating functions into one platform. This makes them ideal for organizations that value ease of management and centralized control.
Common Use Cases for Unified Threat Management
Unified threat management systems are widely used in:
- Small and medium-sized businesses
- Branch offices and remote locations
- Educational institutions
- Healthcare organizations
- Companies with limited IT staff
These environments benefit most from the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of a unified approach.
Future of Unified Threat Management in Cybersecurity
As cybersecurity threats continue to grow, unified threat management systems are evolving to include cloud integration, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics. These enhancements aim to improve threat detection accuracy and adapt to increasingly complex networks.
The core principle of UTM remains the same: simplifying security while maintaining strong protection.
Conclusion
Unified threat management has become a vital component of modern cybersecurity strategies. By combining multiple security functions into a single platform, UTM reduces complexity, improves visibility, and strengthens network defenses.
Understanding the UTM meaning, the unified threat management definition, and how a unified threat management system operates helps organizations make informed decisions about their security infrastructure.
While UTM is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it provides an effective and practical approach to protecting networks in an increasingly dangerous digital world.
FAQs
What is unified threat management?
Unified threat management is a cybersecurity approach that integrates multiple security functions into a single platform to protect networks from various threats.
What is the UTM meaning in cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, UTM refers to a centralized security solution that combines firewall, antivirus, intrusion prevention, and other protective technologies.
Is unified threat management suitable for large enterprises?
UTM can be used in large organizations, but it is often combined with additional specialized security tools for better scalability.
Does a unified threat management system replace all other security tools?
UTM covers many core security needs, but it works best when complemented by endpoint, cloud, and application-level security solutions.
Why is unified threat management important?
Unified threat management simplifies security operations, reduces costs, and provides consistent protection against modern cyber threats.




