Passwords have been the standard way to secure online accounts for decades. However, as digital usage grows, passwords have become one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. Data breaches, phishing attacks, and password reuse have shown that traditional password-based systems are no longer reliable or user-friendly.
Passwordless authentication is an alternative approach that removes the need for users to remember and enter passwords. Instead, it relies on more secure and convenient verification methods. This guide explains what passwordless authentication is, how it works, its benefits, challenges, and how businesses can implement it safely.
What Is Passwordless Authentication?
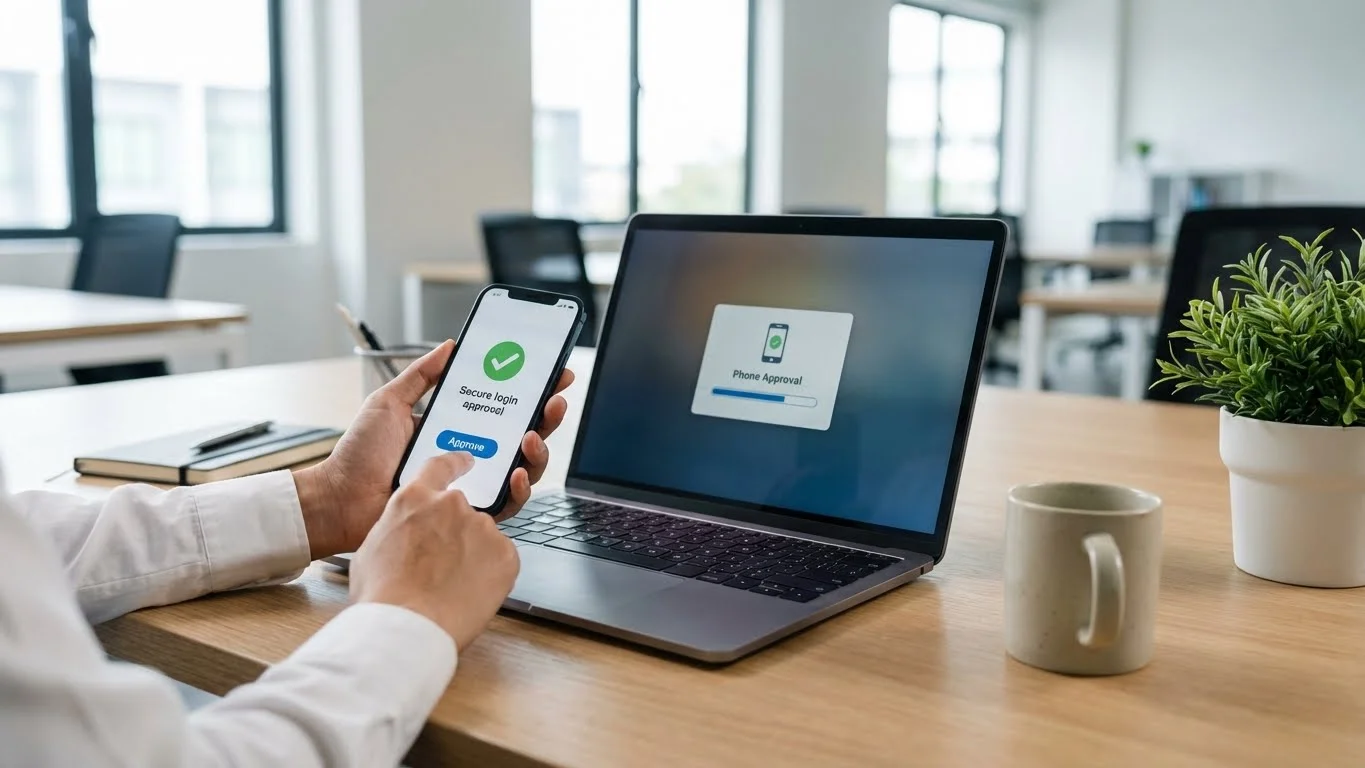

Passwordless authentication is a login method that allows users to access systems, applications, or accounts without entering a traditional password. Instead of something the user knows (a password), it uses other verification factors.
Passwordless systems confirm a user’s identity through secure methods such as biometrics, one-time codes, magic links, or physical devices. The goal is to improve security while making the login experience faster and easier.
In simple terms, passwordless authentication replaces passwords with stronger and more reliable proof of identity.
Why Traditional Passwords Are No Longer Secure
Traditional passwords create multiple security and usability problems. Even strong password policies cannot fully prevent human error or cyberattacks.
Key reasons passwords are no longer secure include:
- Users often reuse the same password across multiple platforms
- Weak or predictable passwords are easy to guess or crack
- Phishing attacks trick users into revealing passwords
- Password databases become valuable targets for hackers
- Resetting forgotten passwords increases IT and support costs
Because passwords rely heavily on user behavior, they remain vulnerable despite security rules and guidelines.
How Passwordless Authentication Works

Passwordless authentication works by verifying a user’s identity using secure authentication factors instead of passwords. The system checks whether the user has or is something unique and trusted.
A typical passwordless login flow includes:
- The user enters an identifier such as an email address or username
- The system sends a verification request (link, code, prompt, or biometric check)
- The user approves the request using a trusted device or method
- Access is granted once verification is successful
Behind the scenes, cryptographic keys and secure communication ensure that authentication data cannot be easily stolen or reused.
Types of Passwordless Authentication Methods

Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication verifies identity based on physical or behavioral traits unique to an individual.
Common biometric methods include:
- Fingerprint scanning
- Facial recognition
- Iris scanning
- Voice recognition
Biometrics are difficult to replicate and eliminate the need to remember credentials, making them both secure and convenient.
Magic Links
Magic links are secure, time-limited login links sent to a user’s email address. Clicking the link automatically logs the user into their account.
Key characteristics of magic links include:
- No password entry required
- Single-use or short expiration time
- Reduced risk of phishing compared to passwords
Magic links are widely used in customer-facing applications because they simplify the login process.
One-Time Passwords (OTP)
One-time passwords are temporary codes generated for a single login session. These codes expire after a short time.
Common OTP delivery methods include:
- SMS messages
- Email messages
- Authenticator apps
OTPs reduce the risk of reused or stolen credentials, though they still depend on secure delivery channels.
Hardware Security Keys
Hardware security keys are physical devices used to authenticate users. They connect via USB, NFC, or Bluetooth.
Advantages of hardware security keys include:
- Strong protection against phishing
- No shared secrets stored on servers
- Physical presence required for login
These devices are often used in high-security environments.
Push Notifications
Push-based authentication sends a login request to a trusted mobile app. The user simply approves or denies the request.
Push notification authentication typically involves:
- A login attempt on another device
- A real-time approval request on a registered mobile device
- One-tap confirmation
This method balances security and convenience, especially for enterprise users.
Passwordless Authentication vs Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwordless authentication and multi-factor authentication are related but not identical concepts.
Key differences include:
- Passwordless authentication removes passwords entirely
- MFA often uses passwords combined with additional factors
- Passwordless focuses on simplicity and reduced friction
- MFA adds layers of security but may still rely on passwords
In practice, passwordless authentication can be part of an MFA strategy, but it does not require a password as the primary factor.
Benefits of Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication offers both security and operational advantages for businesses and users.
Major benefits include:
- Reduced risk of phishing and credential theft
- Faster and simpler login experiences
- Lower password reset and support costs
- Improved user satisfaction and adoption
- Stronger protection using modern cryptography
By removing passwords, organizations eliminate one of the most common attack vectors.
Challenges and Limitations of Passwordless Authentication
Despite its advantages, passwordless authentication is not without challenges.
Common limitations include:
- Dependence on devices like smartphones or hardware keys
- Initial setup and integration complexity
- User resistance to new login methods
- Account recovery issues if devices are lost
Organizations must plan carefully to address these challenges before full adoption.
Use Cases of Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication is used across multiple industries and scenarios.
Common use cases include:
- Employee access to internal systems
- Customer login for websites and mobile apps
- Banking and financial service platforms
- Healthcare portals with sensitive data
- SaaS products requiring secure yet simple access
These use cases benefit from improved security and reduced login friction.
Is Passwordless Authentication Secure?
Passwordless authentication is generally more secure than traditional passwords when implemented correctly.
Security strengths include:
- No stored passwords for attackers to steal
- Use of public and private key cryptography
- Resistance to brute-force and phishing attacks
- Strong device and user verification
Security depends on proper implementation, encryption standards, and secure device management.
How to Implement Passwordless Authentication
Implementing passwordless authentication requires strategic planning and technical readiness.
Key implementation steps include:
- Evaluating business and security requirements
- Selecting suitable authentication methods
- Integrating with existing identity systems
- Testing authentication flows thoroughly
- Training users and support teams
A phased rollout helps reduce disruption and user confusion.
Best Practices for Passwordless Authentication
Following best practices ensures a smooth and secure passwordless experience.
Recommended practices include:
- Offering multiple authentication options
- Providing secure backup and recovery methods
- Ensuring device security and monitoring
- Regularly reviewing authentication policies
These practices help maintain both security and usability.
Passwordless Authentication Trends and Future Outlook
Passwordless authentication adoption continues to grow as organizations prioritize security and user experience.
Key trends include:
- Increased use of biometrics on mobile devices
- Integration with zero-trust security models
- Wider acceptance in consumer applications
- Reduced reliance on legacy password systems
The future points toward a more password-free digital environment.
Conclusion
Passwordless authentication is a modern approach to digital security that removes the risks and frustrations associated with traditional passwords. By relying on secure verification methods, it improves both protection and user experience.
As cyber threats evolve and users demand simpler access, passwordless authentication is becoming a practical and reliable solution for businesses of all sizes. Moving toward passwordless systems is not just a trend, but a necessary step in strengthening digital security.




